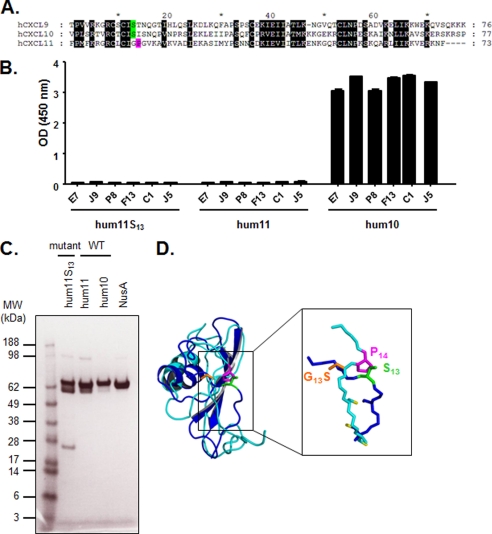
FIGURE 5.
Introduction of Ser13 into CXCL11. A, alignment of mature hCXCL10, hCXCL9, and hCXCL11 chemokine amino acid sequences. Black shaded letters indicate conserved residues according to BLOSUM 62 substitution matrix. Ser13 is represented in green, and Pro14 is indicated in pink. B, specific binding of E7, J9, P8, F13, C1, and J5 dual-specific scFvs to human CXCL11, its mutant, and human CXCL10 was assessed in an ELISA. The indicated NusA-fusion chemokines were captured and then incubated with scFvs. Coating was controlled using specific anti-NusA mAb, and NusA protein was also added to the assay as negative control (data not shown). Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. of duplicates. hum11, human CXCL11; hum10, human CXCL10. C, SDS-PAGE analysis of affinity-purified CXCL11 mutant and wild type, CXCL10, and NusA proteins. The proteins were denatured under reducing conditions and stained with Coomassie Blue. M, Seeblue Plus SDS molecular weight marker (Invitrogen); hum11, human CXCL11; hum10, human CXCL10. D, superimposition of the ribbon representations of monomeric hCXCL10 (dark blue) and hCXCL11 (light blue). The critical amino acid side chains at positions 13 and 14 (Ser13, G13S, and Pro14), and cysteine side chains are represented as sticks in green, orange, pink, and yellow, respectively.