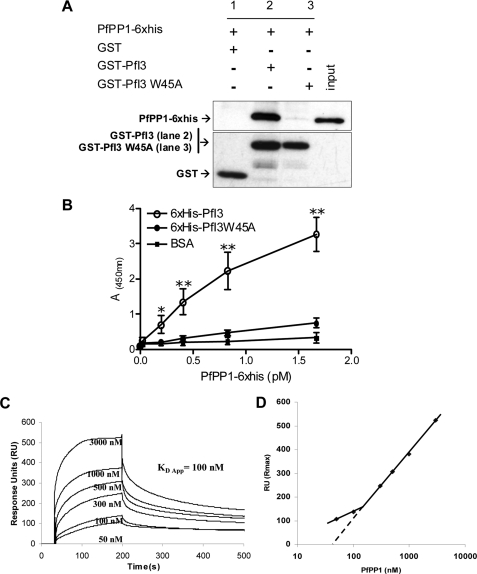
FIGURE 5.
Interaction studies of PfI3 with PfPP1 in vitro. A, GST-pulldown assays. Glutathione-agarose beads coupled with GST alone (lane 1), GST-PfI3 bound to beads (lane 2), or GST-PfI3W45A bound beads (lane 3) were incubated with His6-tagged PfPP1. After washes, proteins bound to the beads were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE and blotted to nitrocellulose. Immunoblot analysis was performed with anti-His mAb (upper blot) and mAb anti-GST antibodies (lower blot) providing loading controls for bound GST and GST-fusion proteins. B, quantification of the binding capacity of PfPP1 to PfI3 using an ELISA-based technique. Increased quantities of biotinylated PfPP1 were added to wells coated with recombinant PfI3 or PfI3W45A proteins (1 μg/well). Results represent experiments carried out with two different batches. Bars indicate S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001 when compared with either BSA or PfI3W45A. C, surface plasmon resonance measurements. PfI3 was immobilized on sensor chip, and increasing concentrations of PfPP1 (50–3000 nm) were used for injections. Base line of each sensogram was normalized and expressed in relative RU. Results shown are representative of three experiments. D, plot of the maximum RU reached in the experiment at each analyte concentration (log scale) shows a biphasic nature that can be explained by the presence of several binding sites of different affinities.