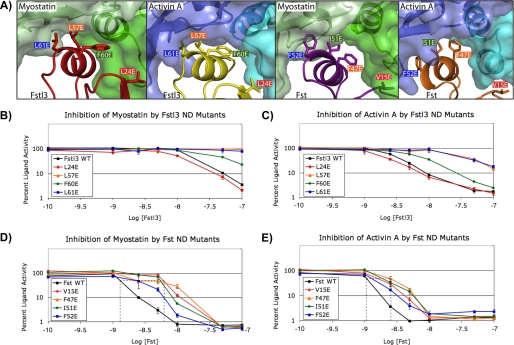
FIGURE 5.
Analysis of the effects of ND point mutations on inhibition of ligands. A, the ligand-ND interface in each complex showing the Fst-type residues that were mutated for luciferase reporter assays (3HH2 (12), 2B0U (28), and 3B4V (25)). Hydrophobic residues were selected as described in the text. Corresponding residues between Fst and Fstl3 are indicated by color coordination of the background of the residue labels. The ND helix residues of Fstl3 complexes are in comparable positions (left two panels), whereas the ND helix of Fst undergoes a conformational rearrangement to reposition side chains depending on which ligand is bound (right two panels). B–E, luciferase reporter assays with myostatin and activin A titrating in either wild-type or ND point mutant Fstl3 or Fst. Line colors correspond to residue label background colors in A. One representative experiment (of a minimum of two repeats) is shown in each panel. The dotted lines in D and E show the approximate IC50 values. The error bars represent ± S.D.