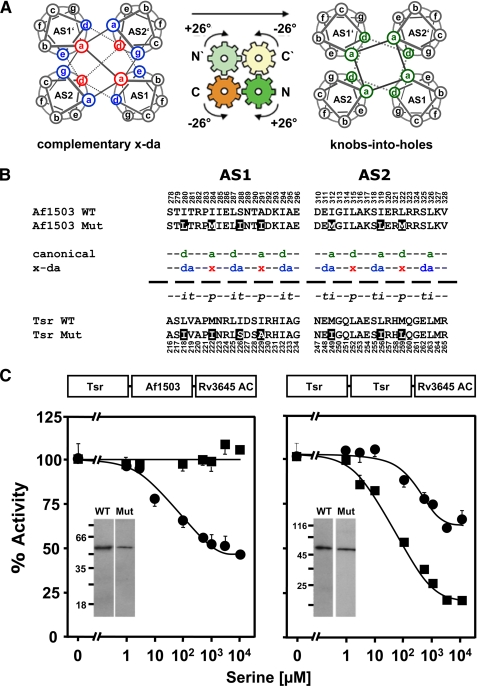
FIGURE 2.
Exchange of x-da exchange residues between Af1503 and Tsr HAMP domains. A, shown is a schematic view of the gearbox model. Helical wheel diagrams show the interconversion from complementary x-da packing (left) to knobs-into-holes packing (right) by a concerted 26° axial rotation of all four helices (indicated by arrows). Complementary x-da packing uses three positions to form the hydrophobic core, one in x-geometry (red) and two in da-geometry (blue; left). Canonical knobs-into-holes packing uses two core residues, both with the same geometry (green; right). B, shown are amino acid sequences of AS1 and AS2 from Tsr and Af1503 HAMP and its mutants. The x-da and canonical (a–g) nomenclature of the differing packing modes is indicated in the middle, with core positions colored and labeled according to their geometries in each packing mode (see above). In addition, the transient, permanent, and intermediate residues are labeled t, p, and i. Residues that were exchanged are inverted. C, serine response of the x-da mutants (circles) compared with the respective unmutated chimeras is shown. Constructs with HAMP from Af1530 are shown on the left and Tsr on the right. 100% activity was 18 ± 0.6 and 19 ± 1.6 nmol of cAMP·mg−1min−1 for Tsr and Af1503 HAMP wild-type chimeras, respectively, and 30 ± 2.3 and 21 ± 1.5 nmol of cAMP·mg−1min−1 for the corresponding mutated chimeras. Western blots of 0.5-μg membrane preparation of each construct are shown as insets. No proteolytic fragments were observed.