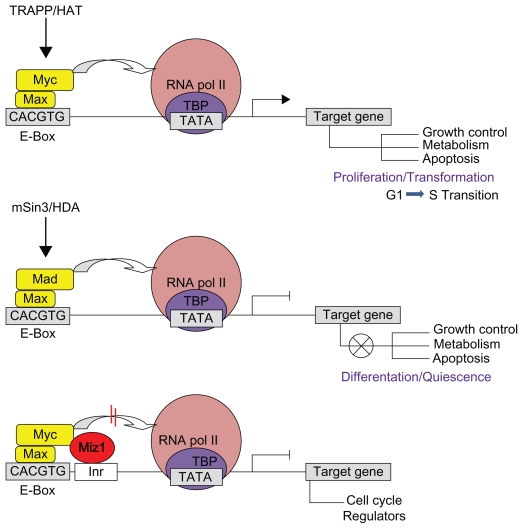
Figure 1.
Simplified schematic interaction of Myc/Myc-associated bHLH proteins at the promoters of target genes. Upon binding to E-box sequences in the promoter region of target genes, heterodimers of Myc/Max can recruit chromatin remodeling complex TRAPP/Histone acetyl-transferase (HAT) and interact with the bound basal transcription machinery at the TATA region of target genes to activate transcription. Conversely, heterodimers of Mad/Max transcription factors recruit mSin3/Histone deacetylases to counteract Myc activity and repress Myc target genes by regulating differentiation and cell cycle arrest. The binding of Myc/Max dimers can interfere with the function of transcription activator Miz-1 to inhibit the recruitment of cofactor proteins like p300 to the promoters of genes responsible for cell cycle regulation.