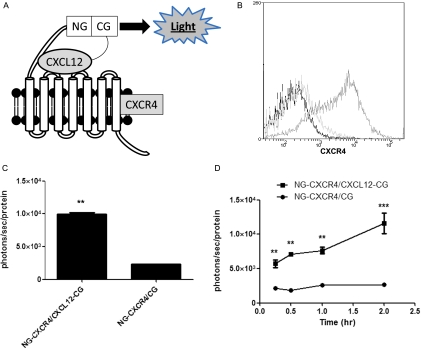
Figure 2.
Gaussia luciferase complementation detects CXCL12-CXCR4 binding in cell-based assays. (A) Schematic diagram of complementation system. The C-terminus of CXCL12 is fused to the C-terminal fragment of Gaussia luciferase (CXCL12-CG), and the N-terminal fragment of Gaussia is fused to the extracellular N-terminus of CXCR4 (NG-CXCR4). These orientations of fusion proteins position NG and CG fragments in the extracellular space. CXCL12 binding to CXCR4 brings together NG and CG enzyme fragments, reconstituting an active enzyme to produce light. (B) Flow cytometry shows expression of CXCR4 on the surface of NG-CXCR4 cells. Dark line indicates unstained; light line, isotype antibody control; and intermediate line, CXCR4 antibody. (C) HeyA8-NG-CXCR4 cells were cocultured with equal numbers of HeyA8-CXCL12-CG (CXCL12-CG/NG-CXCR4) or control cells secreting unfused CG (CG/NG-CXCR4) for 2 hours before quantifying Gaussia luciferase bioluminescence. Photon flux was normalized to relative amounts of total protein per well, and data were expressed as mean values ± SEM for each coculture (n = 4 per condition). (D) Cocultures of HeyA8-CXCL12-CG/NG-CXCR4 or HeyA8-CG/NG-CXCR4 cells were incubated for various periods through 2 hours before quantifying Gaussia luciferase bioluminescence as described in C (n = 4 per condition). **P < .01. ***P < .005.