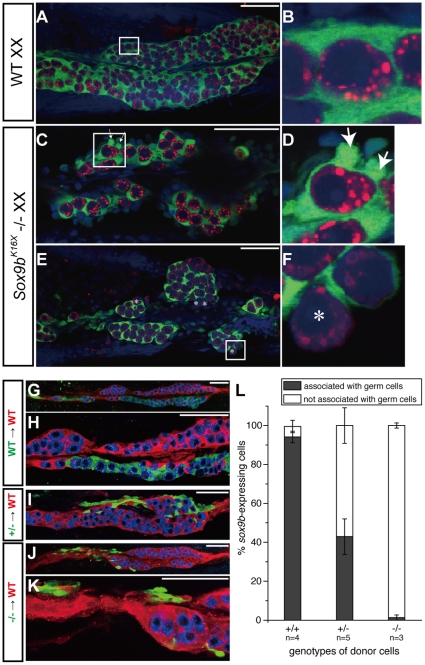
Figure 6. Mutant sox9b-expressing cells demonstrate a reduced cellular association.
(A–F) The morphologies of wild-type (A and B) and mutant (C–F) medaka gonads. Ventral views of XX gonads at 8 dpf (A–D) and 10 dph (E and F) are shown. Green, sox9b-expressing cells were immunostained with anti-GFP; red, germ cells were stained with anti-OLVAS; blue, nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Medaka germ cells are completely surrounded by sox9b-expressing supporting cells and demonstrate a smooth surface (B), whilst mutant sox9b-expressing cells have cytoplasmic protrusions (D, arrows). Some isolated germ cells were not completely surrounded by sox9b-expressing cells in the mutants (F, asterisks). This was not seen in wild-type animals. (G–K) Representative images of somatic chimera. Green, donor-derived sox9b-EGFP expressing cells; red, host sox9b-DsRed positive cells; blue, germ cells stained with anti-OLVAS. (L) Calculated ratio of donor-derived sox9b-EGFP expressing cells associated with germ cells (black) to those not associated with germ cells (white). Scale bar, 50 µm.