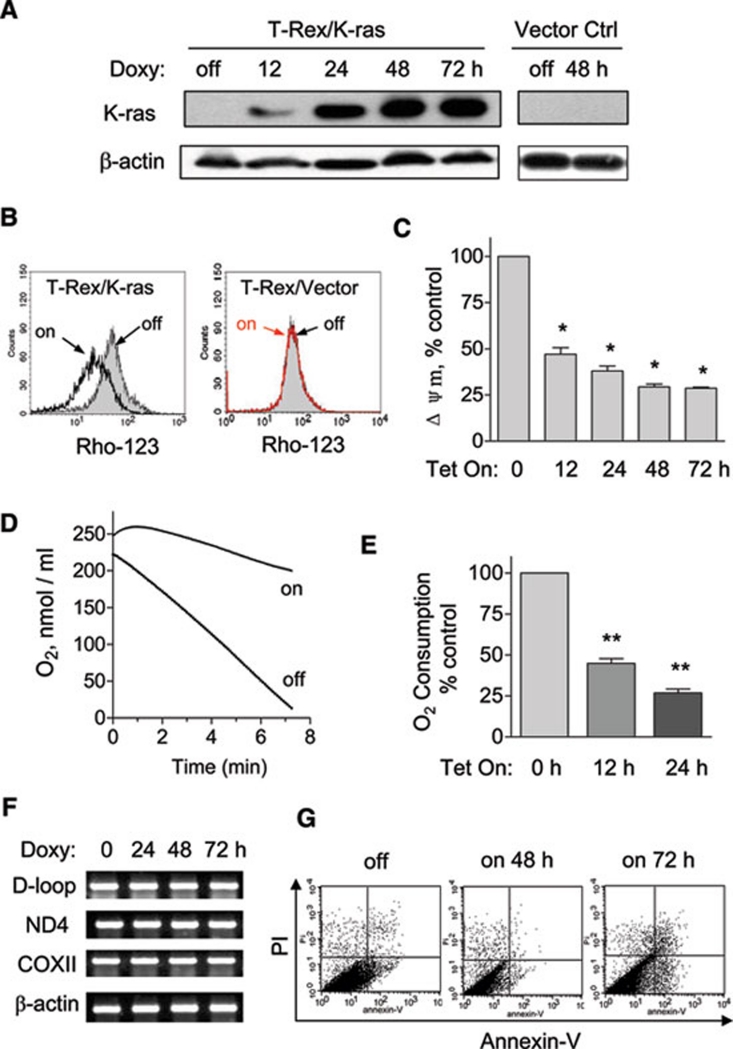
Figure 1.
K-rasG12V activation caused mitochondrial dysfunction. (A) 20 ng/ml doxycycline induced ectopic K-ras expression in T-Rex/K-ras cells in a time-dependent manner. The same doxycycline treatment in T-Rex/Vector control cells caused no significant changes. Protein expression of K-rasG12V was detected by immunoblotting with specific antibody for K-ras. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential in T-Rex/K-ras after K-ras induction by doxycycline for 24 h, measured by fluorescent probe Rho-123. The same concentration of doxycycline caused no effect on transmembrane potential in vector control cells. (C) K-ras activation caused a decrease of mitochondrial transmembrane potential in a time-dependent manner. Transmembrane potential levels of induced cells were normalized to the level of cells without induction. (D) Oxygen consumption rate of T-Rex-293 cells with (Tet/on) and without (Tet/off) K-ras activation for 24 h. (E) K-ras activation inhibited oxygen consumption in a time-dependent manner. (F) K-ras activation did not affect mitochondrial DNA contents. (G) Effect of K-ras activation on cell viability measured by annexin V-PI assay. Data in C and E are shown as mean ± SD. n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.