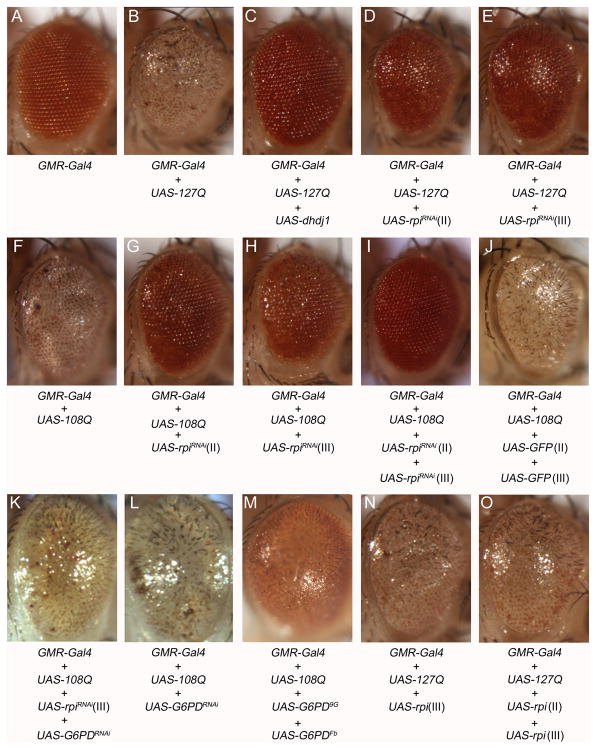
Fig. 5. The knockdown of rpi rescues the polyglutamine-induced rough eyes, and the overexpression of rpi does not further deteriorate the rough eye phenotype.
The eye phenotypes resulting from different combinations of different transgenes of 127Q, 108Q, rpi, G6PD, GFP constructs are shown from A to O. (A) One copy of GMR-Gal4 displayed normal eye appearance as a control. (B) The expression of UAS-127Q by GMR-Gal4 exhibits rough eye phenotype. (C) The expression of UAS-hdj1 rescues the rough eye phenotype (Kazemi-Esfarjani & Benzer 2000), which was used as a positive control. (D, E) The RNAi knockdown of rpi by the transgene on the second (II) or the third (III) chromosome rescues the 127Q-induced rough eye. (F) The expression of UAS-108Q shows similar rough eye phenotype. (G, H) The RNAi knockdown of rpi also rescues the 108Q-induced rough eye. (I) The knockdown of rpi with two copies of UAS-rpiRNAi rescues the rough eye much better than a single copy of UAS-rpiRNAi. (J) The 108Q-induced rough eye cannot be rescued by two copies of UAS-GFP. (K) Knockdown of G6PD blocks the rescue by rpi knockdown on 108Q-induced rough eye. (L) Knockdown of G6PD does not degenerate the rough eye. (M) Overexpression of two copies of UAS-G6PD partially rescues the rough eye. (N) Overexpression of one copy of UAS-rpi does not further worsen the 127Q-induced rough eye. (O) The expression of two copies of UAS-rpi still does not deteriorate the rough eye.