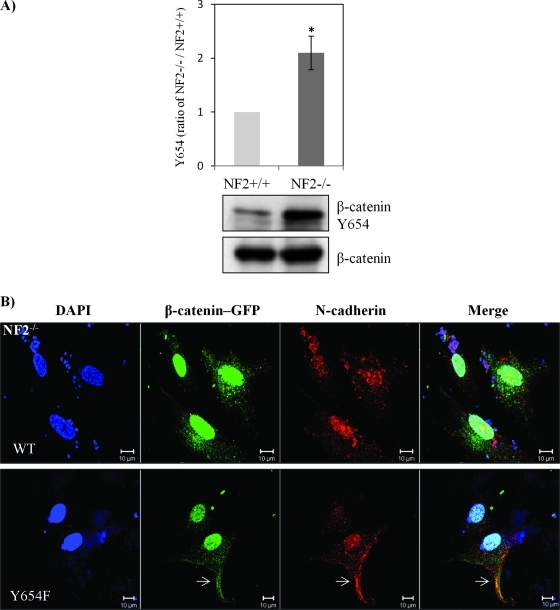
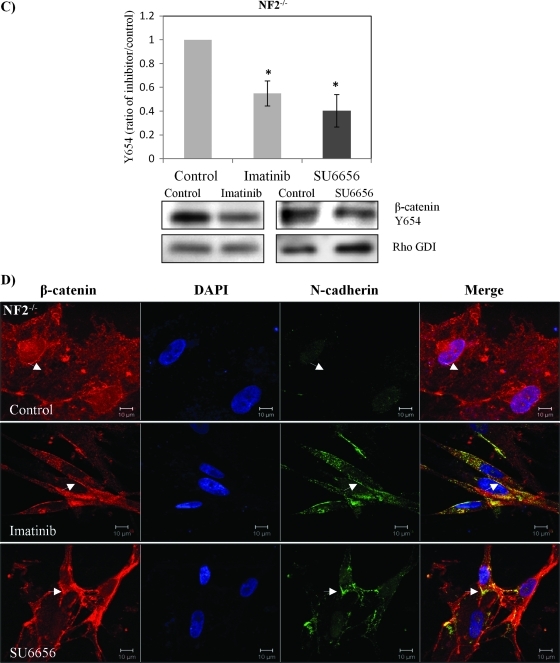
Figure 4.
β-Catenin Y654 phosphorylation is enhanced in schwannoma cells and is mediated by Src and PDGFR at the plasma membrane. (A) β-Catenin Y654 phosphorylation is elevated in schwannomas. Confluent Schwann cells (NF2+/+) and schwannoma cells (NF2-/-) was starved for 24 hours before being treated with pervanadate for 30 minutes to reserve the phosphorylation signals. Western blot analysis was carried out to compare the level of phosphorylation of β-catenin at tyrosine 654. Total β-catenin served as control. Densities of bands were quantified and compared. (B) β-Catenin Y654F relocates N-cadherin to the membrane in schwannoma cells (NF2-/-). Cells were transfected with GFP-β-catenin-WT and GFP-β-catenin-Y654F, respectively. Immunostaining was carried out with DAPI, anti-GFP, and anti-N-cadherin. Scale bar, 10 µm. The sites at the plasma membrane are indicated by arrows. (C) PDGFR and Src inhibitors (imatinib and SU6656) reduced β-catenin Y654 phosphorylation. Schwannoma cells were starved for 24 hours and then treated with DMSO or different inhibitors as well as pervanadate for 30 minutes. Western blot analyses were carried out for β-catenin Y654. RhoGDI was used as a loading control. Densities of bands were quantified and compared. (D) PDGFR and Src inhibitors bring the colocalization of N-cadherin and β-catenin back to the plasma membrane. Cells were treated with control (DMSO), imatinib, and SU6656 for 24 hours. Immunostaining was then carried out with DAPI, anti-N-cadherin, and anti-β-catenin. The potential AJ sites are indicated by arrows. Scale bar, 10 µm.