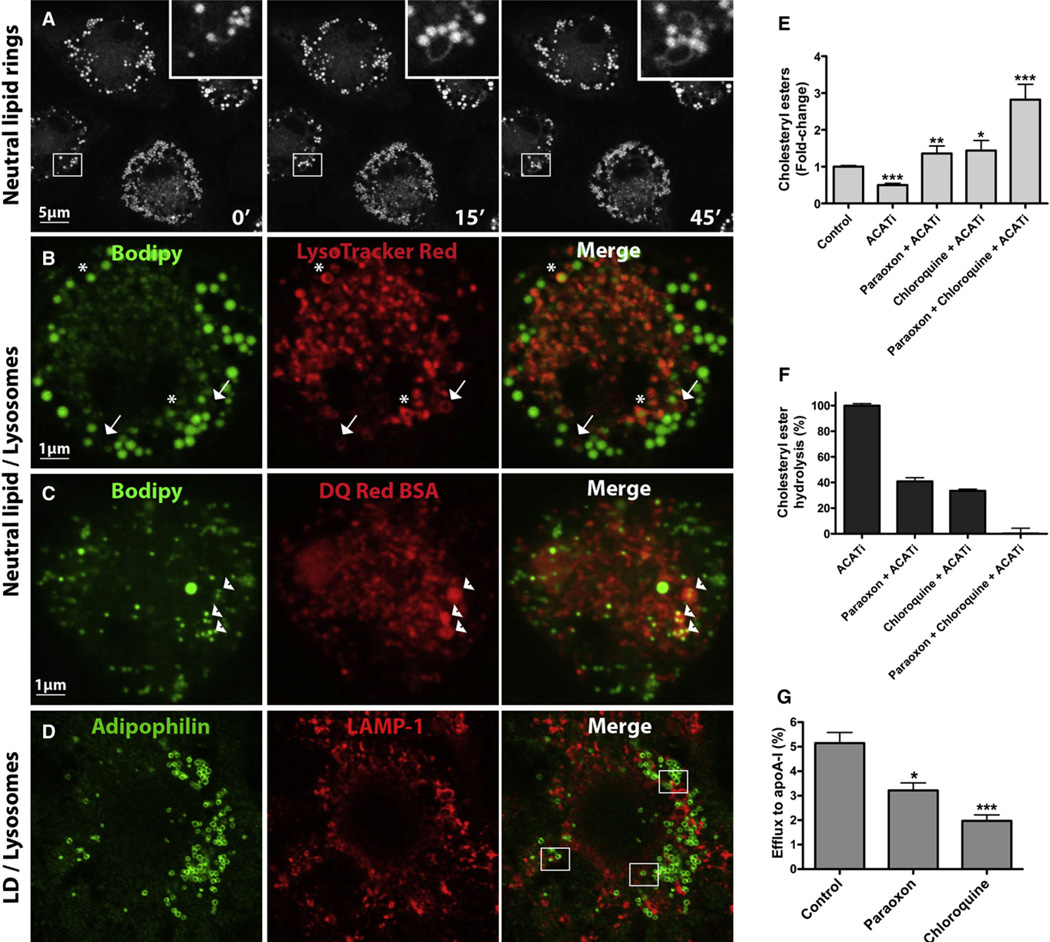
Figure 1. LDs Surround Neutral Lipid Rings and Colocalize with Lysosomes; Inhibition of Lysosomal Function Reduces CE Hydrolysis and Cholesterol Efflux.
(A and B) BMDMs were loaded with AcLDL-derived cholesterol for 30 hr, equilibrated overnight in BSA media, and then incubated with media containing Bodipy (10 µg/mL) with or without LysoTracker Red (50 nM) for 30 min prior to visualization.
(C) Cells were cholesterol loaded as above and then incubated with a BSA conjugate prior to labeling with Bodipy.
(D) Colocalization between the macrophage LD coat protein adipophilin and LAMP-1-positive lysosomes in AcLDL-loaded macrophages.
(E and F) Cellular CE (E) and CE hydrolysis (F) were measured in AcLDL-loaded cells treated with paraoxon or chloroquine for 24 hr in the presence of apoA-I, with or without ACATi. Variations in CE are expressed as fold change relative to control (E) or as a percent CE hydrolysed in 24 hr (F). ***p < 0.0001, **p < 0.001, or *p < 0.005 compared to ACATi, and ACATi was compared to control.
(G) BMDMs were loaded with 3H-cholesterol-AcLDL for 30 hr and equilibrated overnight, and efflux to apoA-I was measured for 24 hr in the presence or absence of paraoxon or chloroquine.