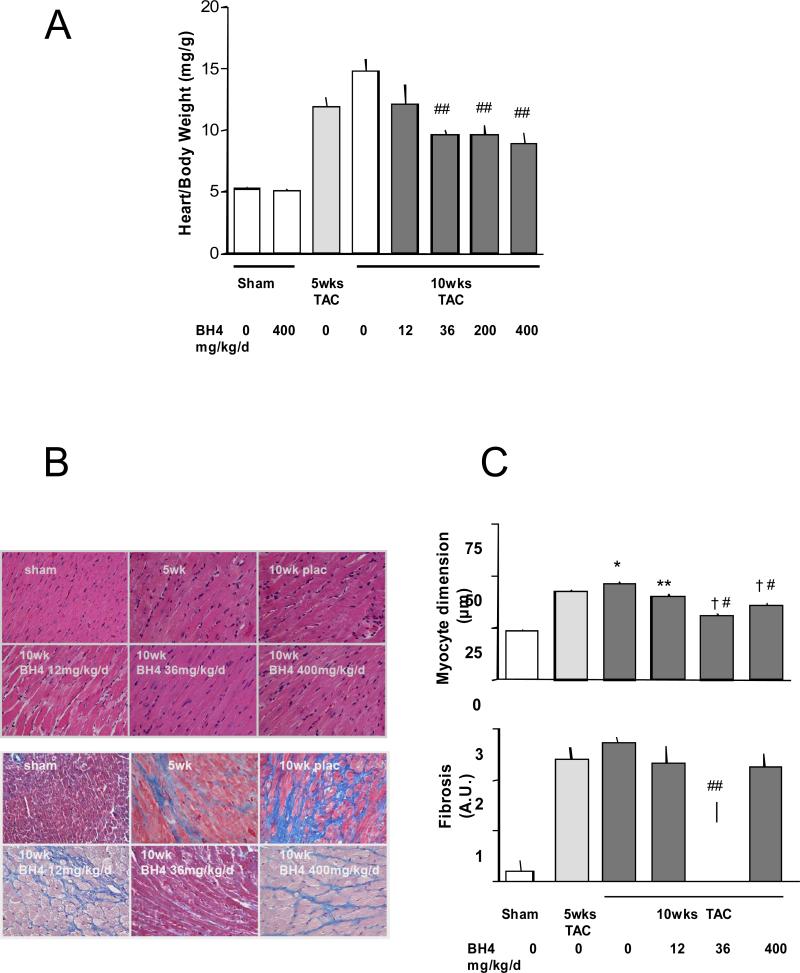
Figure 2.
Exogenous BH4 administration suppresses pre-established cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, but the latter is less effective at low and higher doses. A) Summary data for left ventricular mass (terminal study) normalized to body weight shows reduced hypertrophy with BH4 treatment at doses > 36 mg/kg/d, including the high dose. B) Example histologic sections stained with H/E (upper panels) or Masson trichrome (lower panels) for assessing myocyte dimension and interstitial fibrosis. C) Summary data for histologic analysis. Myocyte hypertrophy was reduced at all BH4 doses, whereas fibrosis was only reduced at the 36 mg/kg/d dose (200 mg/kg/d was not tested in this analysis). *: p<0.05 (versus 5wks); †: p<0.001 (versus 5wks); **: p<0.05 (versus 10wks placebo); #: p<0.001 (versus 10wks placebo). One-way ANOVA with posthoc Bonferoni test on 4 groups.