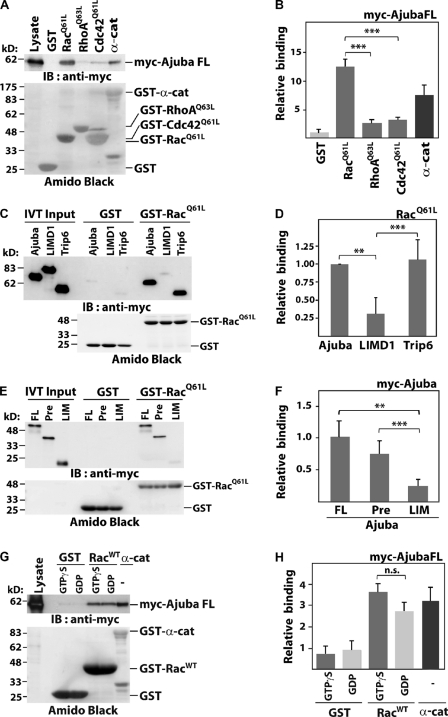
Figure 2.
Ajuba PreLIM interacts directly with Rac in vitro. GST-tagged small GTPases were incubated with (A and G) COS-7 lysates expressing full-length Ajuba, (C and E) in vitro translated Ajuba, or other LIM proteins. Immunoblot of myc-tagged constructs (IB: anti-myc) and GST-proteins as Amido black staining are shown (A, C, E, and G). α-Catenin was used as positive control (A and G). Quantification of experiments is shown as binding relative to GST (B and H) or to Ajuba full-length (D and F). (A and B) Activated forms of Rac (GST-RacQ61L), RhoA (GST-RhoAQ63L), and Cdc42 (GST-Cdc42 [GST-Cdc42Q61L]) were incubated with lysates expressing full-length Ajuba (myc-Ajuba FL). (C and D) Specificity of Ajuba interaction with active Rac. Ajuba, LIMD1, or Trip6 were allowed to interact with GST or GST-RacQ61L. (E and F) Full-length (FL) and Ajuba fragments PreLIM (Pre) or LIM were tested for binding to activated Rac. (G and H) Wild-type Rac (GST-RacWT) was loaded with GTPγS or GDP and incubated with lysates expressing myc-tagged full-length Ajuba. Histograms represent the mean and SD. n = 3. **, P < 0.009; ***, P < 0.005; n.s., nonsignificant.