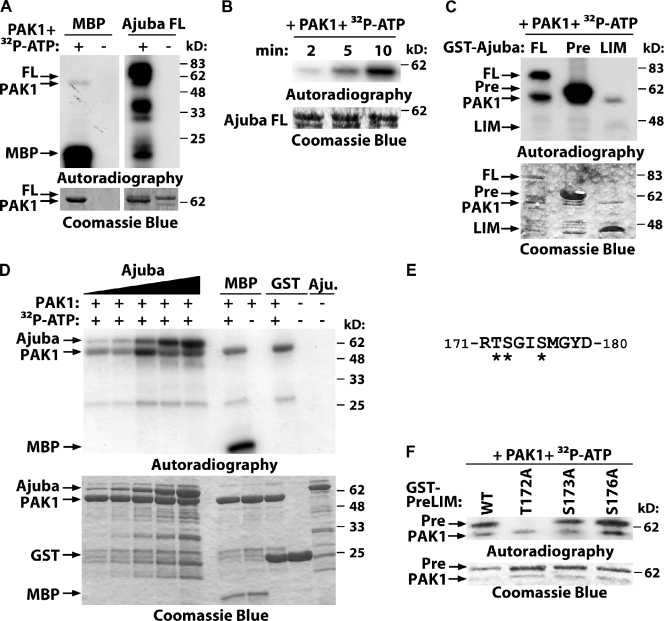
Figure 5.
PAK phosphorylates Ajuba. (A–C) Purified full-length Ajuba (FL) and the truncation mutants PreLIM (Pre) or LIM (LIM) were incubated in vitro with PAK1 kinase domain with or without radioactive ATP (32P-ATP). Phosphorylated bands are shown by autoradiography and fusion proteins by Coomassie blue staining. (A) Full-length Ajuba is phosphorylated by PAK1; MBP was used as positive control; PAK1 auto-phosphorylates itself. (B) Time course of Ajuba phosphorylation. (C) Mapping of Ajuba-phosphorylated region. (D) Different concentrations of Ajuba PreLIM (7.5, 15, 30, 60, and 120 pmol), GST, or MBP were incubated with PAK kinase domain (80 pmol) in an in vitro kinase assay for 5 min. (E) Phosphopeptide isolated after Ajuba phosphorylation by PAK1 using mass spectrometry. Three putative phosphorylation sites are shown (asterisks). (F) PAK1 phosphorylates Ajuba at residue 172. Different alanine mutations were prepared in Ajuba PreLIM region (T172A, S172A, or S176A) and GST fusion proteins phosphorylated in vitro by PAK1.