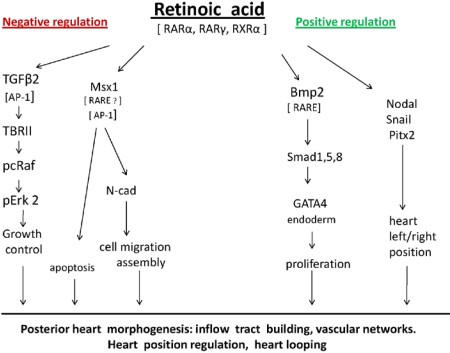
Figure 1.
Potential retinoic acid signaling pathways involved in building the early embryonic heart. Retinoic acid (RA) is an embryonic morphogen, participating in heart morphogenesis. The effects of RA are mainly mediated by RA as the ligand for the transcription factors RARs. TGFβ2 [125] and Msx-1 [106,107] both have AP-1 sites in their promoters, that are negatively regulated by RA/RAR blocking AP-1 activity [6,11,125]. Potential binding sites for RAR/RXR have been identified in the Msx1 promoter [105,106,107]. Genes containing the RA responsive element, RARE, such as Bmp2 [137], are direct RA target genes, regulated by RA/RAR/RXR heterodimers. The potential signaling pathways are based on research data obtained in M. Zile’s laboratory [83].