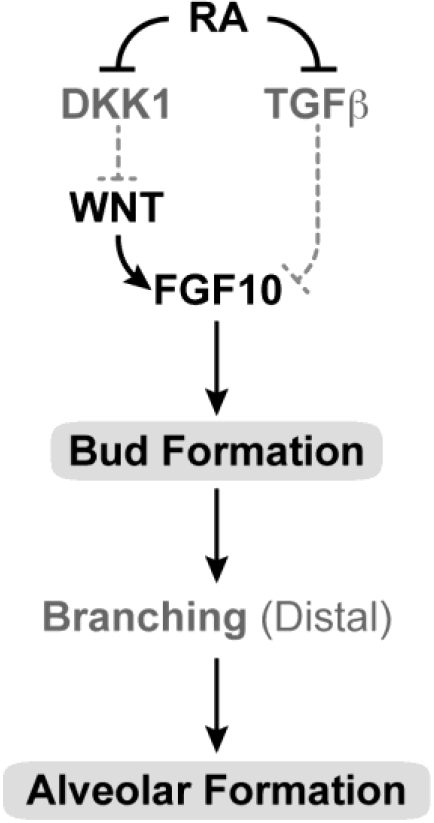
Figure 6.
Schematic showing the proposed sites of RA action in lung development. In the developing embryo, RA is needed for primary bud formation (grey oval), but signaling is down-regulated during the time that lung differentiation occurs. A later role for RA in alveolar formation (grey oval) is also proposed. During induction of the lung buds, RA regulates mesodermal Fgf10 levels by negatively regulating Tgfβ and enabling induction of the Wnt pathway by repression of the Dickkopf homolog 1 (Dkk1) known to antagonize Wnt ligand-receptor binding. RA may also influence the response of the foregut endoderm (origin of lung progenitors) to Fgf10. (Adapted from [262]).