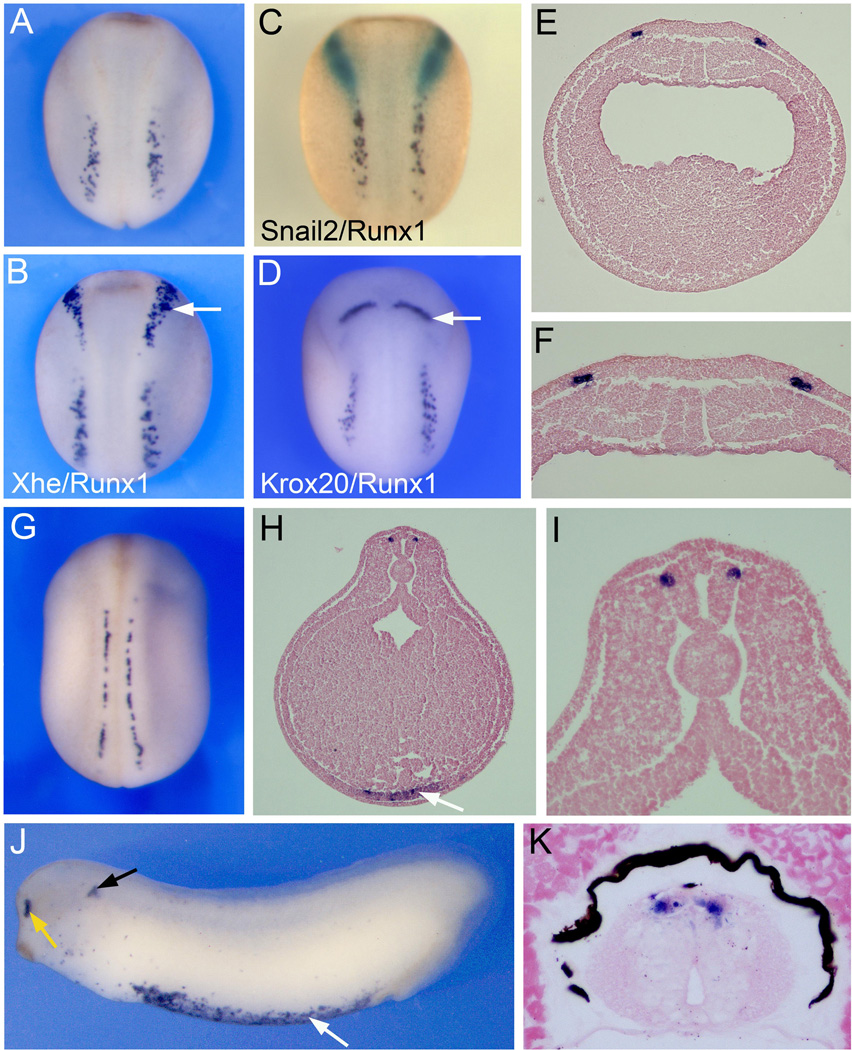
Figure 1. Expression of Runx1/Xaml1 in Rohon-Beard sensory neurons by whole-mount in situ hybridization.
(A–F) Runx1 expression in stage 15 embryos. (A) Runx1 is detected at the posterior portion of the NPB. (B) Double in situ hybridization for Runx1 and the HG marker Xhe. Runx1 positive cells are located posterior to HG cells (arrow). (C) Double in situ hybridization for Runx1 and the neural crest marker Snail2. Runx1 expression (purple) is distinct from and posterior to the neural crest forming region (Snail2, green staining). (D) Double in situ hybridization for Runx1 and the hindbrain marker Krox20 (arrow). Panels (A–D), dorsal view, anterior to top. (E) Transverse section, dorsal to top, showing that Runx1 is restricted to two discrete domains at the neural plate border. (F) Higher magnification of the neural plate region of the embryo shown in (E). (G) At stage 22 as the neural tube closes, Runx1 expression is restricted to the dorsal aspect of the spinal cord. Dorsal view, anterior to top. (H–I) Transverse section through a stage 23 embryo, dorsal to top. Runx1 is confined to the dorso-lateral region of the spinal cord. Runx1 is also detected ventrally in the lateral plate mesoderm, precursor of the hematopoietic lineage (arrow). (I) Higher magnification of the neural tube region of the embryo shown in (H). (J) Runx1 expression in a stage 28 embryo. Runx1 is detected in the olfactory epithelium (yellow arrow), periotic mesenchyme (black arrow), and blood precursors (white arrow). Lateral view, anterior to left. (K) Transverse section through the spinal cord of a stage 45 embryo shows Runx1 expression in RB sensory neurons in the dorsal spinal cord. Dorsal to top.