Fig. (3).
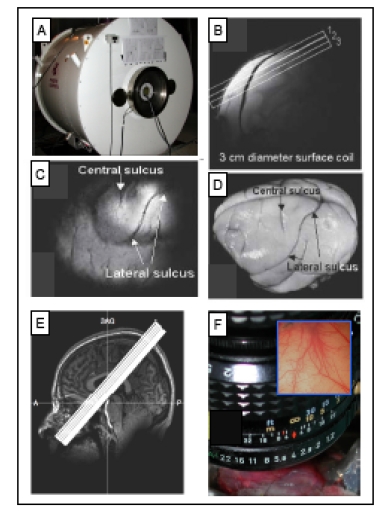
Methods used for imaging the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). A. 9.4 T MRI imaging with a 21-cm bore Varian Inova MR system (Varian, Palo Alto, CA). B. A high-resolution scout coronal image is collected to guide, parallel to SI, placement of three oblique slices (slice locations indicated by white overlaid rectangles). C. The most superficial slice image acquired with T2* weighting, where sulci and vascular structures appear dark, allow ready identification of both the central and lateral sulci (white arrows). D. Major landmarks (such as central and lateral sulci) used to identify SI are visible on the surface of post-mortem squirrel monkey brain. E. 7 T Philips Achieva magnet with a 16-channel NOVA head coil is used to collect oblique coronal image slices. Sixteen oblique coronal images slices were positioned to cover SI, SII, posterior insula and thalamus. A = anterior, P = posterior, SAG = sagittal. F. Intrinsic optical imaging with 632 nm light. An optical window made with agar and a slide coverslip covers a craniotomy. Inset illustrates a typical field of view of 6x6 mm2 of SI cortex.
