Figure 2.
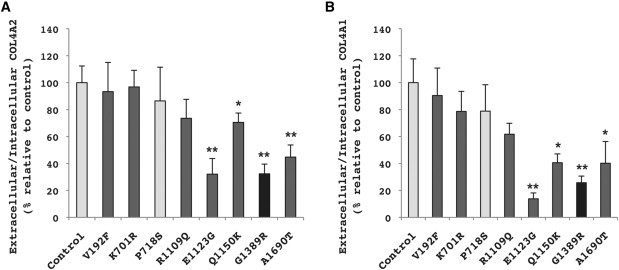
Functional Assay Reveals that COL4A2E1123G, COL4A2Q1150K, and COL4A2A1690T Impair COL4A2 and COL4A1 Secretion
Ratios of extracellular to intracellular COL4A2 (A) or COL4A1 (B) from cells expressing different COL4A2 alleles were determined by immunoblot analysis and are expressed as a percent relative to control (NM_001846.2) COL4A2 cDNA (mean of five independent experiments ± standard error of the mean [SEM]). The highly polymorphic common variant COL4A2P718S was used as a presumptive negative control, and the pathogenic mutation COL4A2G1389R was used as a positive control of the functional assay. The variants COL4A2V192F, COL4A2K701R, or COL4A2R1109Q have no functional consequences on the biosynthesis of COL4A1/COL4A2 heterotrimers. The COL4A2E1123G, COL4A2Q1150K, and COL4A2A1690T variants significantly reduce the extracellular to intracellular ratio of COL4A2 and COL4A1, suggesting that they are pathogenic mutations (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01). The control cDNA and a common polymorphism are shown in light gray, the known pathogenic variant is shown in black, and the rare variants identified in the patient cohort are shown in dark gray.
