Figure 3.
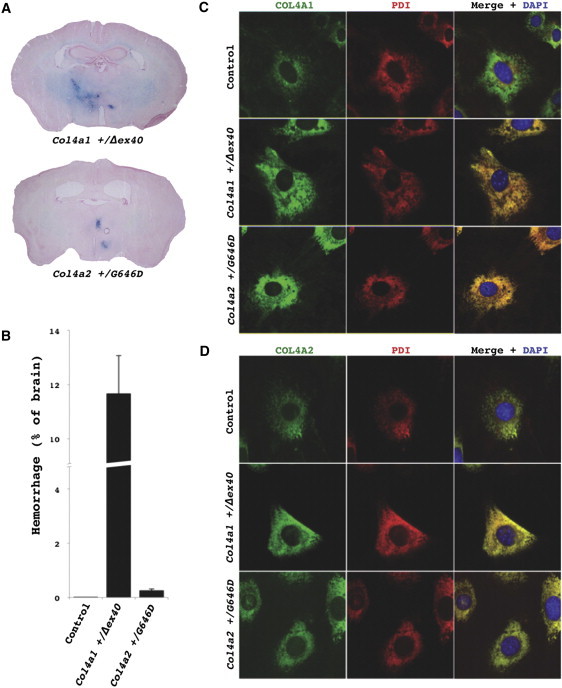
Col4a2 Mutant Mice Have Intracerebral Hemorrhages and Retention of COL4A1/A2 Heterotrimers within the ER
(A) Prussian Blue staining of brains from Col4a2+/G646D mutant mice revealed multifocal ICHs in all mutant mice (n = 5) and none in control mice (C57BL/6J Col4a1+/+; Col4a2+/+, n = 7, data not shown). The extent of the ICH appeared much less severe than ICH detected in Col4a1+/Δex40 mutant mice.
(B) To compare the severity of ICH between the two mutant lines, we measured the proportional area of ICH in brain sections at regularly spaced intervals (mean ± SEM). Control (C57BL/6J) mice never had detectable ICH and ICHs in Col4a2+/G646D mutant mice were much less severe than those observed in Col4a1+/Δex40 mutant mice.
(C and D) Immunofluorescent labeling of COL4A1 or COL4A2 (rat H11 or rat H22 [1:200], respectively, with AlexaFluor488 anti-rat IgG [1:500], Invitrogen; green) and the ER marker PDI (mouse ID3 [1:500], Stressgen with AlexaFluor594 anti-mouse IgG [1:500], Invitrogen; red) was performed in MEFs.38 MEFs were grown on glass coverslips, serum-deprived and treated with ascorbic acid (50 μg/ml) for 24 hr, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton in PBS. Cells were then mounted with Mowiol containing 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) to label nuclei. Colabeling with PDI and anti-COL4A1 (C) or anti-COL4A2 (D) in control (C57BL/6J Col4a1+/+; Col4a2+/+) cells showed considerable COL4A1/A2 labeling that did not colocalize with PDI and therefore was not within the ER. In contrast, in Col4a1+/Δex40 or Col4a2+/G646D mutant cells all of the detectable COL4A1 and COL4A2 labeling was colocalized with the ER marker, indicating ER retention of the COL4A1 and COL4A2 proteins. All animal experiments were done with the approval of the UCSF institutional animal care and use committee.
