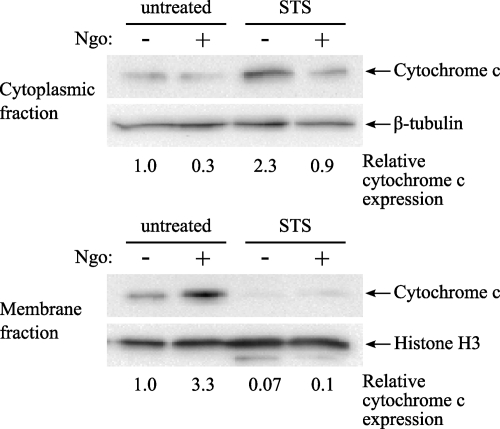
Fig. 5.
N. gonorrhoeae inhibits cytochrome c translocation to the cytoplasm. Differentiated HL-60 cells were infected with N. gonorrhoeae at an MOI of 20 for 3 h and then were left untreated or were treated with 1 μM STS for a further 3 h. The cells were subjected to cellular fractionation to separate cytoplasmic proteins from membrane-associated proteins. Both cytoplasmic and membrane fractions were subjected to Western blotting using an antibody directed against cytochrome c, and antibodies directed against β-tubulin and histone H3 were used as loading controls. The results are representative of 4 independent experiments.