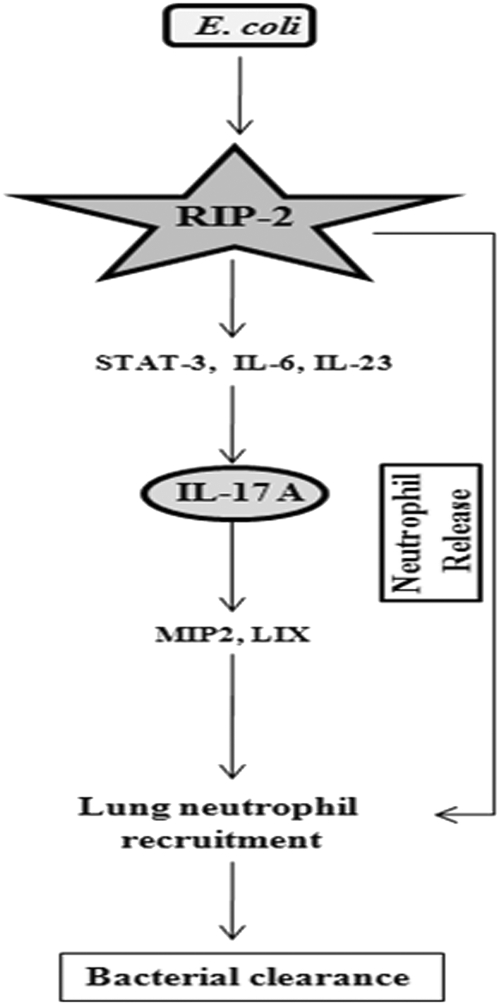
Fig. 7.
Schematic depicting the role of RIP2 in neutrophil recruitment and release during E. coli infection. E. coli infection induces IL-17A production through RIP2-mediated STAT3 activation and IL-6 and IL-23 production. IL-17A in turn regulates the production of CXC chemokines (MIP-2 and LIX) and neutrophil release, resulting in neutrophil recruitment and subsequent bacterial clearance in the lungs. Furthermore, RIP2 plays an essential role in neutrophil release from the marrow during pulmonary infection with E. coli.