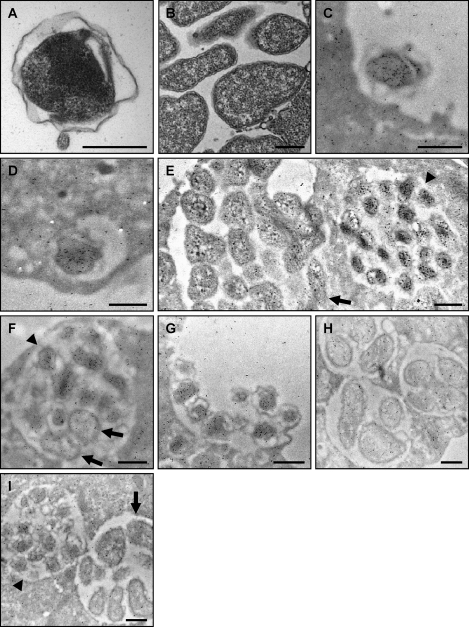
Fig. 6.
Assessment of APH_1235 expression by immunoelectron microscopy. (A and B) Reference transmission electron micrographs of a DC (A) and multiple RC organisms (B) are provided because the fixation method that is requisite for immunoelectron microscopy compromises the clarity by which the distinctive DC and RC outer membranes can be discerned. (C to H) A. phagocytophilum-infected HL-60 cells were fixed and screened with anti-APH_1235 followed by goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to 6-nm gold particles and examined by electron microscopy. Representative results of up to four experiments are shown. (C) A DC organism bound to the surface of a HL-60 cell. (D) At 40 min postinfection, a newly internalized DC organism is detected within a host cell-derived vacuole. (E) Two adjacent morulae. The morula on the left harbors RC organisms, while that on the right contains DC bacteria. (F) A morula harboring many DC organisms and two bacteria that are still in the RC form. (G) Remnant of an A. phagocytophilum-occupied vacuole that has ruptured at the host cell surface and from which DC organisms are being released. (H) Three morulae harboring RC bacteria at 18 h postinfection. (I) Two morulae harboring either DC (left) or RC (right) organisms screened with preimmune serum followed by goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to 6-nm gold particles and examination by electron microscopy. (E, F, and I) Arrowheads denote individual DC bacteria or entire morulae consisting of DC organisms. Arrows denote single RC bacteria or entire morulae comprised of RC organisms. Scale bars, 0.5 μm.