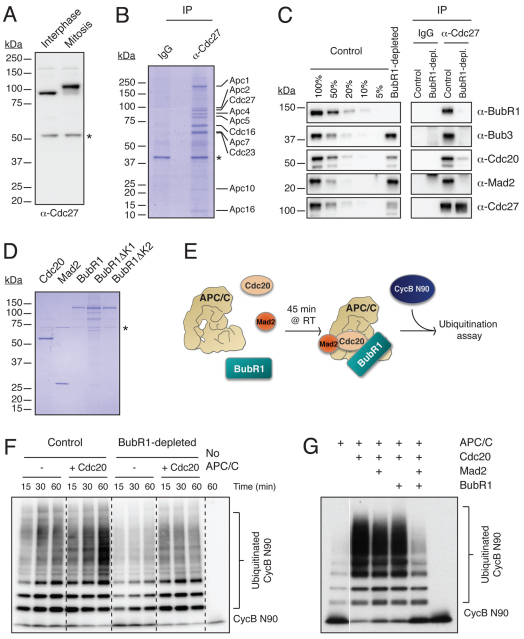
Fig. 5.
Measuring APC/C ubiquitylation activity in vitro. (A) Immunoblot of HeLa cell lysates probed with the anti-Cdc27 antibody (RC27.3). (B) Colloidal Coomassie Blue gel of anti-Cdc27 immune complexes isolated from asynchronous HeLa cells indicating the APC/C subunits identified by mass spectrometry. The asterisk denotes a non-specific band. (C) Immunoblots of Cdc27 immune complexes isolated from mitotic extracts, with or without prior immunodepletion of BubR1. Membranes were blotted with antibodies against BubR1, Bub3, Mad2, Cdc20 and Cdc27. Dilutions of the control-depleted extract were included to estimate the immunodepletion efficiency. (D) Coomassie Blue gel of purified Cdc20, Mad2 and BubR1 proteins. The asterisk denotes a contaminant band. (E) Schematic showing the in vitro ubiquitylation assays. (F) Immunoblot of an APC/C ubiquitylation assay probed with anti-Myc antibodies to detect cyclin B1 N90 conjugates. Note that prior depletion of BubR1 reduces the basal activity of the APC/C. (G) Immunoblot of a ubiquitylation assay showing that only the combination of Mad2 and BubR1 can inhibit Cdc20-mediated activation of APC/C.