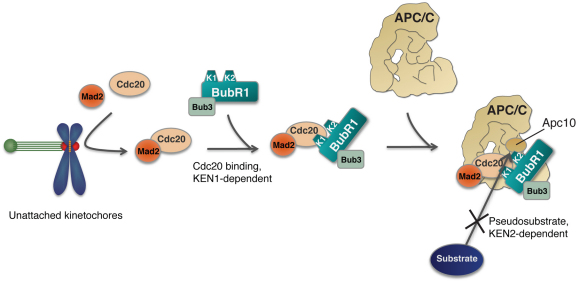
Fig. 8.
Schematic explaining how the two KEN boxes in BubR1 promote MCC assembly and APC/C inhibition. The Cdc20–Mad2 subcomplex is generated at unattached kinetochores, and then binds the BubR1–Bub3 subcomplex in a KEN1-dependent manner to form the MCC. In turn, the MCC then binds the APC/C and inhibits substrate recruitment in a KEN2-dependent manner, possibly by occupying the substrate-binding pocket between Cdc20 and Apc10.