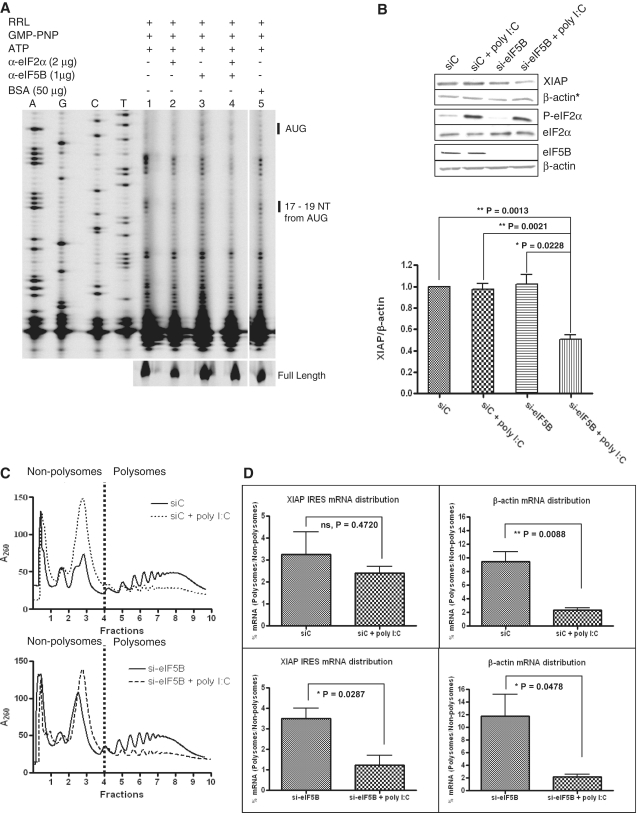
Figure 5.
Translation initiation on XIAP IRES RNA switches to an eIF5B-dependent mode when eIF2 is inactivated. (A) A quantity of 5 μl of RRL was incubated with the anti-eIF2α and/or anti-eIF5B antibodies at 4°C overnight. Following the immuno-inactivation of the indicated initiation factors, the toeprinting assay of the XIAP IRES initiation complex was performed. (B) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with siRNA targeting eIF5B or non-targeting control siRNA and poly I:C as indicated. Western blot analysis (upper panel) was performed to verify eIF5B knockdown and phosphorylation of eIF2α, and the levels of endogenous XIAP protein. XIAP levels are represented as the ratio of XIAP to β-actin (lower panel; n = 4, mean ± SEM). The actin blot used for XIAP normalization is indicated with an asterisk. (C) Polysome profiling of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with siRNA targeting eIF5B or non-targeting control siRNA and poly I:C as indicated. Non-polysome (translationally inactive) and polysome (translationally active) fractions are separated by broken vertical lines. Representative profile of three independent experiments is shown. (D) Individual fractions were probed for the presence of β-actin and IRES-containing endogenous XIAP mRNAs by qRT–PCR. Percent distribution of specific mRNAs relative to the spiked CAT RNA control across the gradient was determined. The amount (%) of specific mRNA present in polysomes relative to non-polysomes quantifies the change in translation efficiency (n = 3, mean ± SEM).