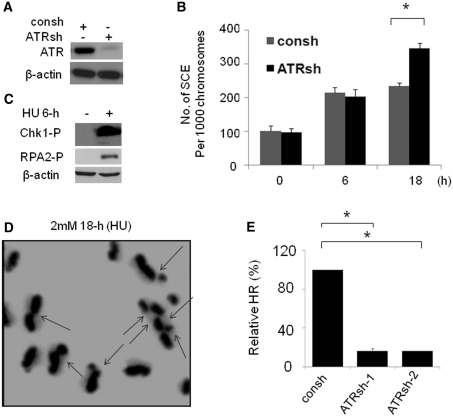
Figure 2.
ATR suppresses the SCE induced by replication fork collapse. (A) ATR knockdown by shRNA targeting ATR (ATRsh). Lysates were prepared from MCF7 cells after 72-h infection with ATRsh or control shRNA (consh). (B) The SCEs induced by collapsed DNA replication forks are suppressed by ATR. At 48-h after infection with ATRsh, MCF7 cells were used for SCE assay, which is performed as described in Figure 1C. The data shown is the result from three independent experiments. P-values were calculated by Student's t-test (*P < 0.01). (C) Chk1 phosphorylation (Chk1-P) and RPA2-P (anti-RPA2-p4/8 antibody) are increased in cells treated with 2 mM HU for 6-h. Actin was detected as a load control. (D) Representative metaphase prepared in MCF7 cells treated with 18-h HU following ATR depletion by ATRsh. The chromosomes with SCE(s) were indicated by arrows. (E) ATR-deficient cells show significant reductions in HR mediated by short tract gene conversion. HR induced by I-Sce-I was measured by dual-color flow cytometric detection of GFP-positive cells. The relative HR frequencies in cells depleted of ATR are shown in comparison to cells with intact ATR expression. Results are means from three independent experiments, with standard errors shown. P-values were calculated by Student's t-test (*P < 0.01).