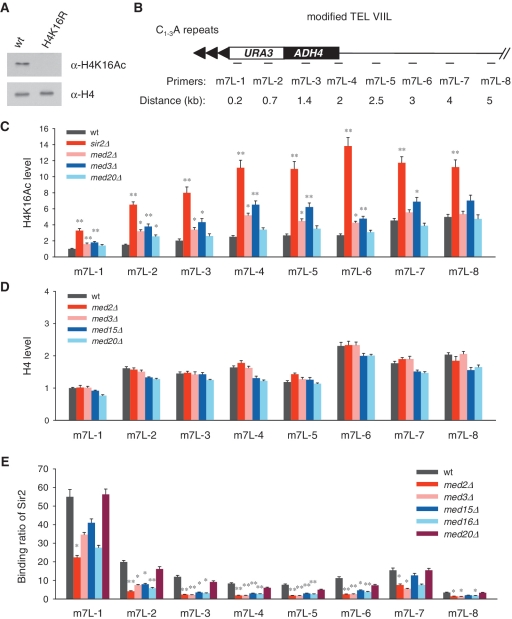
Figure 3.
H4K16 acetylation increases and Sir2 binding is reduced at modified telomere VIIL in Mediator tail mutants. (A) Specificity of anti-H4K16Ac antibody was verified. Chromatin of wild-type and H4K16R mutant cells was extracted and subjected to western blot. (B) Schematic diagram of the modified telomere VIIL (m7L) and the locations of primers used in ChIP assay. (C) ChIP results of H4K16 acetylation level on telomere m7L. The wild-type value at the most distal locus (m7L-1) is arbitrarily set to 1 where the acetylation level is supposed to be the lowest. The statistical significances of difference in H4K16 acetylation between mutants and wild-type cells are provided (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). (D) H4 level is detected by ChIP assay. The wild-type value at m7L-1 is set to 1. (E) Binding of 13Myc-tagged Sir2 on m7L was detected by ChIP assay using anti-Myc antibody.