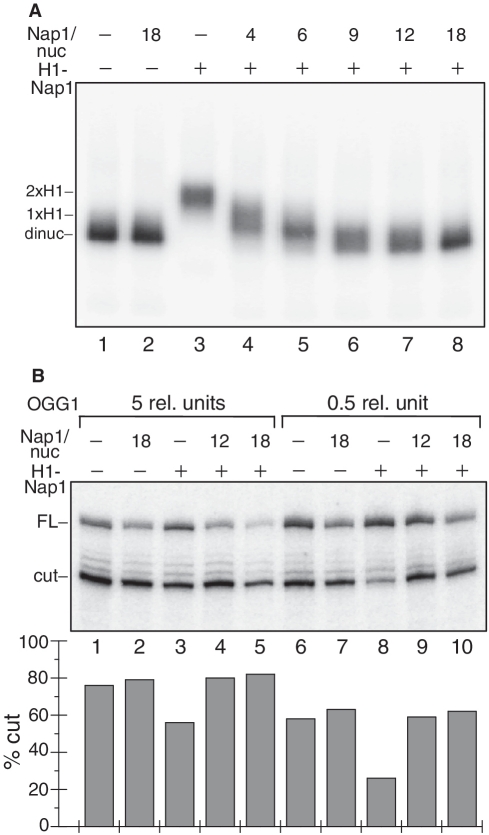
Figure 4.
NAP-1 mediated removal of histone H1 restores the efficiency of OGG1 to cleave 8-oxoG in the dinucleosomal linker DNA. (A) NAP-1 is able to remove histone H1 from the dinucleosomal template. 32P-end labelled 20-bp linker DNA dinucleosomes containing histone H1 were incubated with increasing excess of NAP-1 over nucleosomes as indicated and the mixture was run on a 1% agarose del (lanes 4–8). Nap1/nuc represents the molar ratio that does not take into account the 2-fold NAP-1 excess already present after H1 deposition. Lanes 1 and 2: dinucleosomes without histone H1. Note the increase of the electrophoretic mobility of the dinucleosomes upon increasing the concentration of NAP-1. (B) OGG1 Cleavage efficiency of 8-oxoG within the dinucleosome linker DNA. 32P-end labelled dinucleosomes without histone H1 (lines 1, 2, 6, 7) or with H1 (lines 3–5, 8–10) were incubated with an excess of NAP-1 over nucleosomes as indicated and then treated with either 0.5 (lanes 6–10) or with 5 U (lanes 1–5) of OGG1 for 90 min. The cleavage reaction products were separated on 8% denaturing gel. The dried gel was processed by a Phosphoimager (Fuji-Fla 5100) (upper panel). The position of the full length (FL) and cleaved (cut) DNA are indicated. The quantification of the data is shown on the lower panel. The relative SD is ±9% for line 8 and ±4–5% for all other lines.