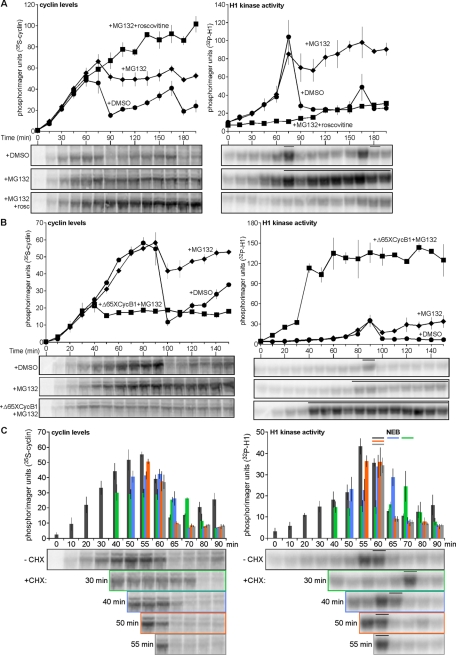
FIGURE 2:
Inhibiting or prematurely activating CDK1 alters the level of cyclin B synthesis. (A–C) Time course of cyclin B levels (left) and H1 kinase activities (right) for cycling extracts treated with (A) DMSO (1%) and ethanol (0.64%), MG132 (1 mM) and ethanol, or MG132 (1 mM) and roscovitine (0.18 mM); (B) DMSO (1%) and buffer, MG132 (1 mM) and buffer, or MG132 (1 mM) and Δ65XCycB1 (200 nM); (C) CHX (100 μg/ml) added at different time points prior to and during mitosis in cycling egg extract. Data were shifted to align the peak H1 kinase activities of all three replicates, with one replicate shifted 5 min earlier, excluding the earliest and latest lone time points from the analysis. Data were analyzed as described in Figure 1A and plotted as means ± SEM (A, N = 3; B, N = 2; C, N = 3). Bars denote time points where NEB was observed (A–C), and histograms correspond to cyclin levels and H1 kinase activities before and after CHX addition (C); control (no addition), dark gray bars; 30 min addition, light green bars; 40 min addition, light blue bars; 50 min, orange bars; 55 min, light gray bars.