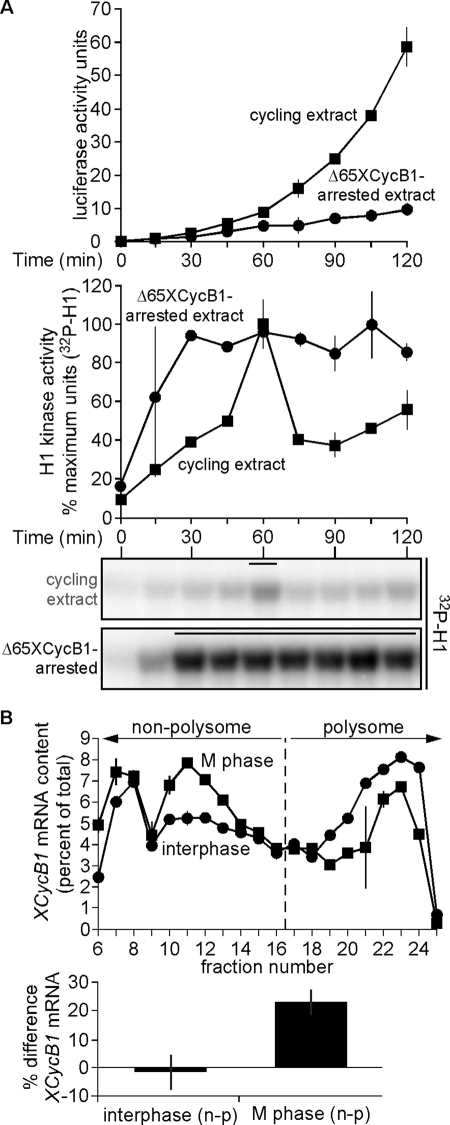
FIGURE 5:
A reduction of cyclin B1 mRNA content in polysome fractions at M phase corresponds to its diminished translation. (A) Luciferase mRNA is poorly translated in mitosis-arrested extract. In vitro–transcribed luciferase mRNA (5 ng/μl) was added to cycling extracts treated with either buffer or Δ65XCycB1 (200 nM). Samples were collected at 15-min intervals in a 96-well plate cooled on ice, and luciferase assays were then performed. H1 kinase activities were analyzed as described in Figure 1A (bottom) and plotted with luciferase signals as means ± SEM (N = 2; top), in cycling egg extract (boxes), and Δ65XCycB1-arrested extract (dots). Data were shifted to align the H1 kinase activity peaks of both replicates, with one replicate shifted 15 min earlier, excluding the earliest and latest lone time points from the analysis. Bars above H1 kinase activities denote time points where NEB was observed. (B) Top, samples of interphase extract and mitotic extract (just prior to NEB) were separated by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Total RNA from 40S, 60S, 80S, and polysome fractions was purified, and the distribution of cyclin B1 mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Left of the dashed line is defined as nonpolysome fraction (40S, 60S, and 80S) and on its right is defined as the polysome fraction. The percentage cyclin B1 mRNA in each fraction was quantitated and normalized as a percentage of total across all fractions, in duplicate. (B) Bottom, differences in the percentage of cyclin B1 mRNA in nonpolysome and polysome fractions (n − p) between interphase and mitosis is presented as mean ± SEM (N = 3). Also see Supplemental Figure S5.