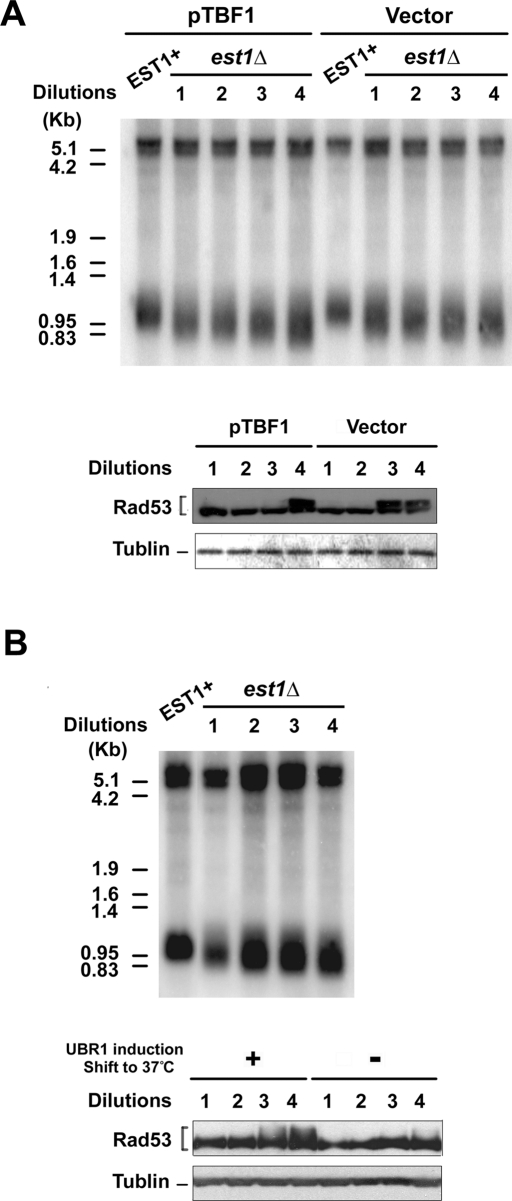
FIGURE 9:
Effect of Tbf1 depletion on checkpoint response to short telomeres. (A) Effect of Tbf1 depletion on checkpoint response in telomerase-deficient cells. Telomerase-deficient est1Δ tbf1-d (KSC2867) cells carrying YCpT-TBF1 or the control vector were obtained from the strain carrying the URA3-marked EST1 plasmid. Colonies arisen on plates containing 5-FOA were grown to the late log phase. The culture was diluted fourfold to allow cells to undergo cell division twice for 7 h at 30°C. This cycle was repeated four times. Cells from each serial dilution culture were synchronized at G2/M with nocodazole. Aliquots of cells were harvested to monitor the telomere length by Southern blots (top). Cells were incubated with galactose at 37°C to degrade Tbf1-d protein. After 3 h of incubation cells were harvested to monitor Rad53 phosphorylation by immunoblotting with anti-Rad53 antibodies (bottom). Tubulin was detected as a loading control. (B) Effect of Tbf1 depletion on checkpoint response in telomerase-deficient cells. Telomerase-deficient est1Δ tbf1-d (KSC2867) cells were obtained after streaking the strain carrying the URA3-marked EST1 plasmid. Colonies arisen on plates containing 5-FOA were grown to the late log phase. Cells were continuously grown after dilution and then synchronized with nocodazole at 30°C as in A. Aliquots of cells were harvested to monitor the telomere length by Southern blots (top). After synchronization, half of the rest was incubated with galactose at 37°C to degrade Tbf1 protein. The other half was incubated with glucose at 30°C to retain Tbf1 expression. After 3 h of incubation, cells were harvested to monitor Rad53 phosphorylation as in A.