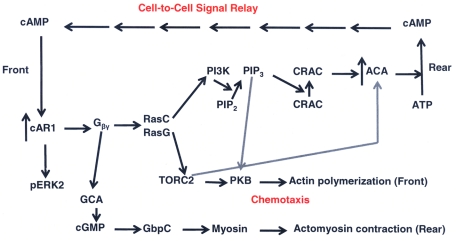
FIGURE 1:
Schematic depiction of cAMP signaling pathways in D. discoideum. cAMP binding to G protein–coupled cAR1 increases the expression of cAR1 and ACA and the release of Gβγ, which activate RasC and RasG pathways. Activation of PI3K leads to phosphorylation of PIP2, and PIP3 brings CRAC to the plasma membrane, activating ACA, which converts ATP to cAMP, which is secreted at the rear and binds to cAR1 of neighboring cells. Activation of TORC2 activates PKB, which initiates actin polymerization at the front of the cell. TORC2 also contributes to the activation of ACA, and PIP3 contributes to PKB activation. Gβγ also activates GCA, which synthesizes cGMP, which, acting through GbpC, contributes to myosin activation and actomyosin contraction at the rear of the cell. cAMP-bound cAR1 also phosphorylates and activates ERK2, which contributes to ACA activation. Not all of the intermediates in these pathways are shown.