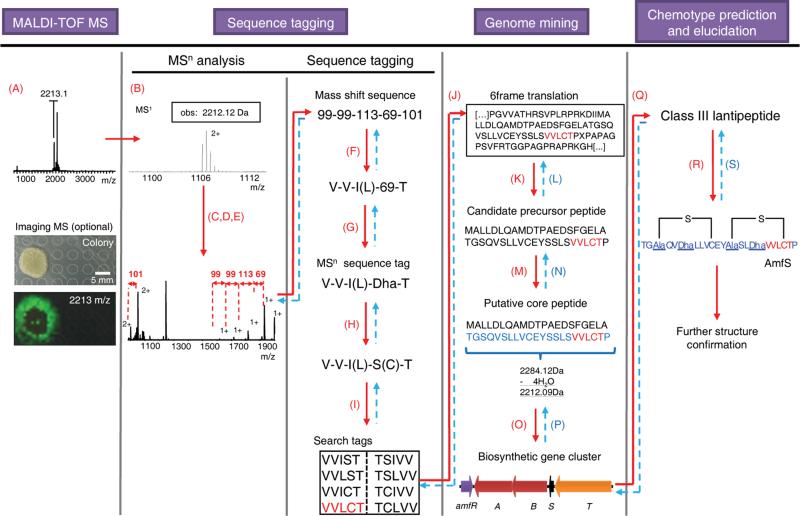
Figure 3. Peptidogenomic connection of a ribosomal peptide (RNP) chemotype with its biosynthetic genes (genotype) via sequence tagging and genome mining – Characterization of class III lantipeptide AmfS from Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350.
Iterative aspects in connecting MS data of the peptide chemotype to the genotype are highlighted in blue and in dashed arrows. Steps are as follows: (A) Detection of putative peptide mass signals by MALDI-TOF MS or Imaging MS, (B) determination of molecular weight, (C) MSn fragmentation (CID), (D) assignment of charge states, (E) identification of mass shifts, (F) substitution of proteinogenic mass shifts (Supplementary Table 5), (G) substitution of nonproteinogenic mass shifts with putative RNP monomers (Supplementary Table 6), (H) MSn sequence tag processing of putative biosynthetic or MS gas-phase modifications, (I) MSn sequence tag processing of sequence tag direction, (J) search in 6-frame translation of target genome, (K) identification of candidate precursor peptide via RNP biosynthetic rationale, (L) verification of precursor peptide sequence, (M) prediction of core peptide sequence based on observed mass and putative PTM mass shifts, (N) verification of core peptide sequence and mass, (O) prediction of biosynthetic gene cluster, (P) verification of putative PTMs, (Q) RNP classification, (R) structure prediction based on RNP class and MSn data, and (S) structure verification by MSn data.