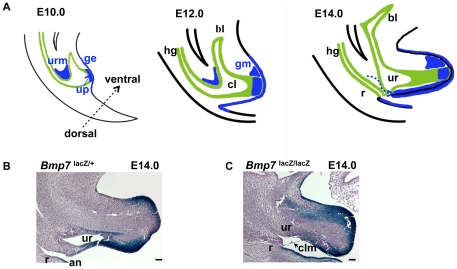
Figure 1. Time-line of normal cloacal partitioning in the mouse (A), and arrest in cloacal septation in Bmp7 null embryo (C compare to B).
(A) Domains of Bmp7 expression in the urorectal mesenchyme (URM), urethral plate (up), and genital ectoderm (ge) are shown in blue. Cloacal endoderm is in green. At E10, the ventral part of the cloaca (cl) extends rostrally to give rise to the embryonic urogenital sinus and the primordium of the bladder (bl). At E12, Bmp7 expression appears in the dorsal genital mesenchyme (gm). At E14, Bmp7 expression in the URM shifts to the ventral portion of the genital tubercle (dashed arrow). (B, C) Histological sagittal sections of normal Bmp7lacZ/+ (B) and Bmp7lacZ/lacZ null embryos (C) stained with X-gal. Heterozygous embryo (B) shows normal position of the rectum (r) and anus (an). In Bmp7lacZ/lacZ null embryo (C), a hypoplastic rectum and urethra (ur) open into a common cloacal orifice covered by the cloacal membrane (clm). Scale bars: 100 µm.