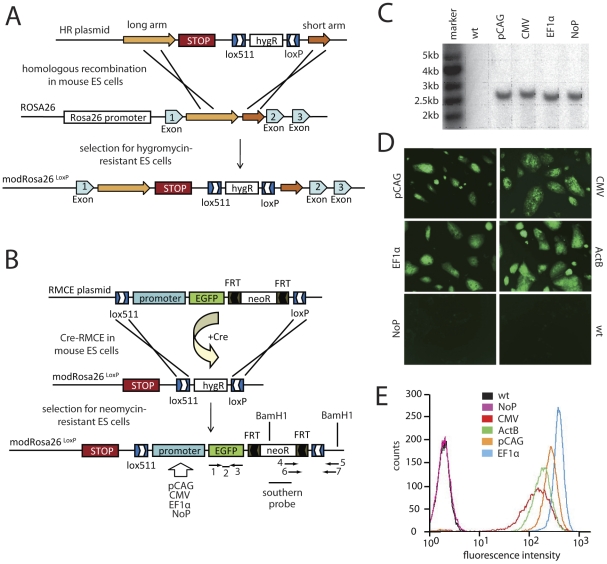
Figure 1. Generation of mice with a modified Rosa26 locus (modRosa26LoxP) and testing of different promoters.
(A) Scheme depicting the generation of the modRosa26LoxP in ES cells. A Stop sequence and a HygR selection cassette flanked by heterospecific LoxP sites (Lox511 and LoxP) were targeted to the Rosa26 locus between exons 1 and 2 by homologous recombination. After successful recombination, the Stop cassette is located downstream of the endogenous Rosa26 promoter. (B) Cre-RMCE into the modRosa26LoxP locus. In the Cre-RMCE targeting plasmid, a promoter, EGFP and an FRT-flanked neomycin selection cassette (NeoR) were flanked by heterospecific LoxP sites (Lox511 and LoxP) as a group. Cre-RMCE was used to replace the HygR in the modRosa26LoxP ES cells with the Lox511/LoxP-flanked sequence in the RMCE targeting plasmid. A pCAG, CMV or EF1α promoter driving EGFP was introduced. Insertion of EGFP without any promoter (NoP) controls for functional shielding of the integration site from the endogenous Rosa26 promoter. Binding regions for TaqMan genotyping primers (1, 3) and probe (2), primers for checking integration into the modRosa26LoxP locus (4–7) and the Southern hybridization probe, as well as the BamHI sites used for Southern blot analysis are indicated. (C) Southern blot analysis on genomic DNA-derived ES cell lines shows specific integration into the modRosa26LoxP locus. A 2.4-kb BamHI fragment was detected using a Neo probe. mR26-pCAG-EGFP, mR26-CMV-EGFP, mR26-EF1α-EGFP and mR26-NoP-EGFP ES cells show successful targeting of the modRosa26LoxP locus, without additional integrations at random sites. Wt ES cells show no signal. (D) Modified ES cells showing strong EGFP fluorescence. The pCAG, EF1α and CMV promoters drive strong EGFP expression in the modRosa26LoxP in vitro. ES cells without promoter but with EGFP inserted into the modRosa26LoxP locus do not show EGFP fluorescence, indicating functional shielding of the integration site from the endogenous Rosa26 promoter. (E) FACS analysis in mR26-NoP-EGFP ES cells showed no EGFP fluorescence when compared to wt ES cells. mR26-EF1α-EGFP ES cells showed the highest EGFP fluorescence, followed by mR26-pCAG-EGFP, ActB and mR26-CMV-EGFP ES cells.