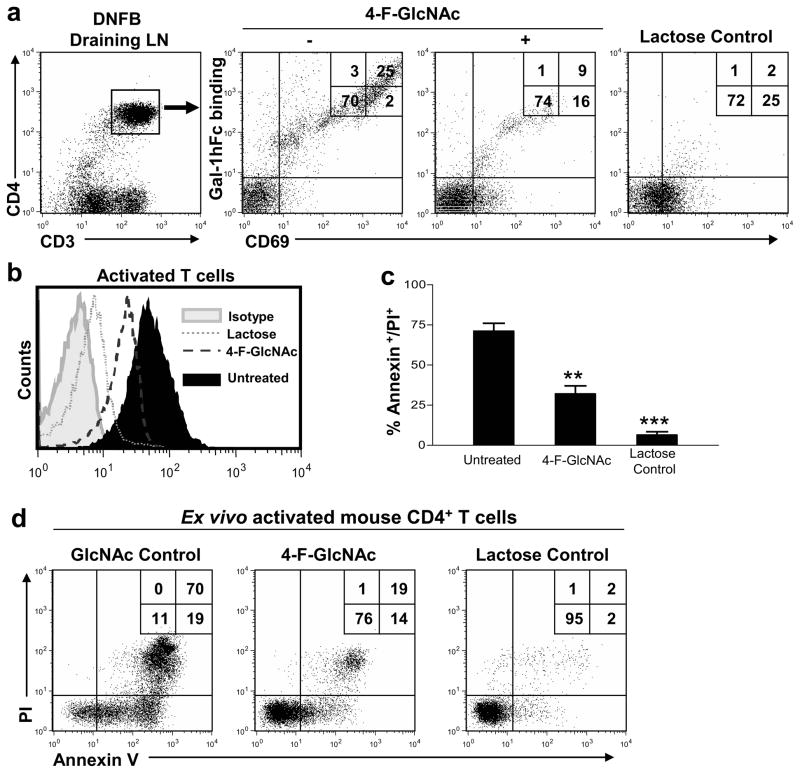
Figure 2. 4-F-GlcNAc-mediated reduction of Gal-1-binding N-acetyllactosamines prevents Gal-1-mediated T cell death.
(a) Gated CD4+ T cells from DNFB-draining LNs in mice treated with 4-F-GlcNAc or GlcNAc control were analyzed for Gal-1hFc binding and CD69 expression by flow cytometry. (b) Naïve CD4+ T cells were activated ex vivo for 48h +/− 15μM 4-F-GlcNAc. Cell binding to Gal-1hFc was analyzed in the presence or absence of lactose by flow cytometry. (c) Activated CD4+ T cells were incubated with 2.5μM Gal-1hFc for 24h, and cell death was evaluated by Annexin V staining/PI uptake and graphically represented from 3 experiments in (d). Statistically significance difference compared with untreated cells by Student’s paired t-test, **p<0.001 and ***p<0.0001.