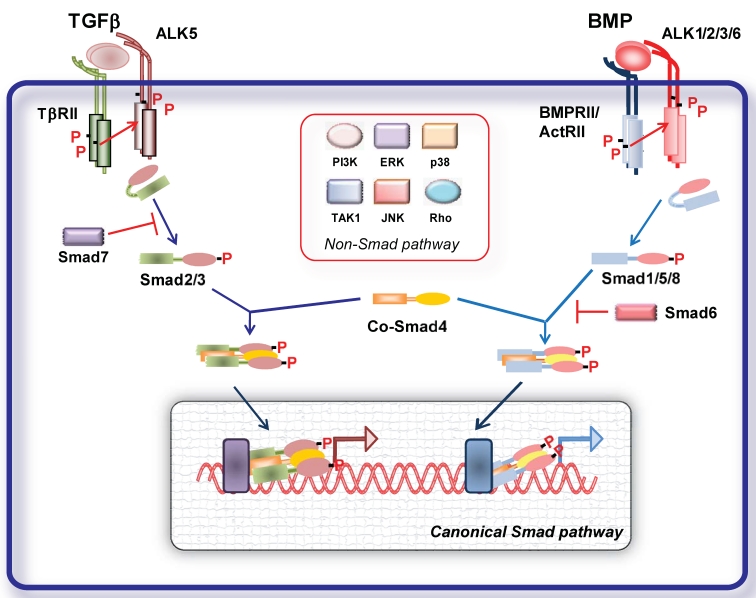
Figure 1.
Signal transduction by TGFβ family members. TGFβ and BMP dimers induce heteromeric complex formation between specific type II and type I receptors. The type II receptors then transphosphorylate the type I receptors, leading to their activation. Subsequently, the type I receptor propagates the signal into the cell by phosphorylating receptor-regulated (R)-Smads, which form heteromeric complexes with Smad4 (common (Co)-Smad) and translocate in the nucleus where by interacting with other transcription factors regulate gene transcriptional responses (canonical Smad signaling pathway). Inhibitory (I) Smads 6 and 7 inhibit receptor activation of R-Smads. In addition, the activated type I receptors can activate non-Smad pathways (non-Smad signaling pathway).