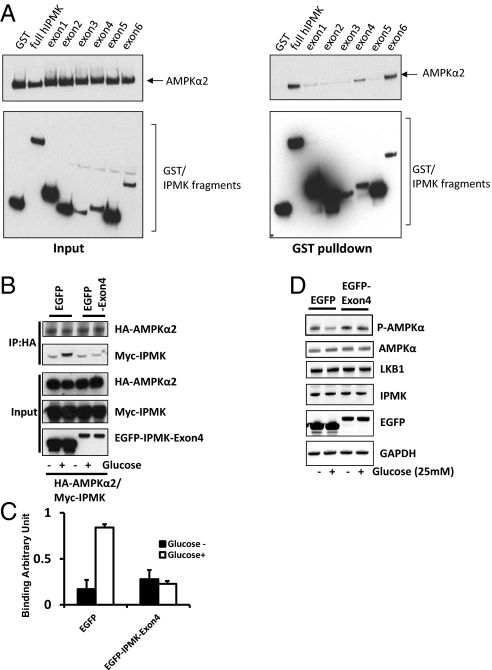
Fig. 3.
Physical interaction between IPMK and AMPK is required for IPMK-mediated modulation of AMPK. (A) Mapping of binding region of IPMK responsible for AMPK interaction. GST, GST-IPMK or GST–IPMK exon fragments (exon 1: 1–62, exon 2: 63–92, exon 3: 93–124, exon 4: 125–182, exon 5: 183–208 and exon 6: 209–416) were pull-downed from HEK293T cells cotransfected with AMPKα2. Coimmunoprecipitation of AMPKα2 was determined by Western blots. (B–D) Dominant-negative IPMK exon 4 disrupts the IPMK-AMPK interaction. (B) HA-AMPKα2, Myc-IPMK, and EGFP or EGFP-IPMK exon 4 were cotransfected into GT1-7 cells as indicated. Cells were deprived of glucose for 3 h and stimulated with glucose for 30 min before lysis. HA-AMPKα2 was immunoprecipitated and coimmunoprecipitates of Myc-IPMK were determined by Western blot (C) Relative quantifications of bound AMPKα2 and IPMK levels are shown. Values are expressed as means ± SD of three determinations (*Student t test; P < 0.005). (D) EGFP or EGFP-exon 4 was transfected into HEK293 cells as indicated. Cells were deprived of glucose for 3 h and stimulated with or without glucose for 30 min before lysis. Proteins were extracted and analyzed by Western blotting.