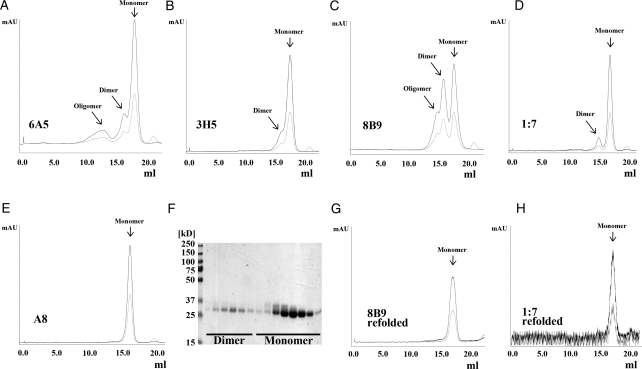
Fig. 2.
Purification of human and murine scFvs. ScFvs 6A5 (A), 3H5 (B), 8B9 (C), 1:7 (D) and A8 (E) were affinity purified and subsequently SEC was performed using a Superdex 200 column. Chromatograms show absorption at 280 nm (black) and 254 nm (light grey) and reveal for the majority of the scFvs a major peak corresponding to a monomeric scFv (∼26 kD). In addition, particularly for scFv 8B9 (C), but less pronounced also for scFvs 6A5, 3H5 and 1:7 (A, B, D) a second peak was observed, which corresponds to a dimeric scFv (or diabody). For scFv 8B9 and scFv 6A5 (A, C) a minor peak was detected corresponding to oligomeric scFv. (F) SDS–PAGE analysis of SEC elution fractions of scFv 1:7 under non-reducing conditions confirms the diabodies to be indeed non-covalent dimers. Fractions corresponding to diabodies of scFvs 8B9 and 1:7 were pooled separately, refolded as described in the Materials and methods section and analyzed again by SEC. The SEC profiles of refolded scFvs 8B9 (G) and 1:7 (H) clearly demonstrate a shift of the elution peak of the diabodies toward a monomeric scFv indicating an efficient and successful refolding.