FIGURE 3.
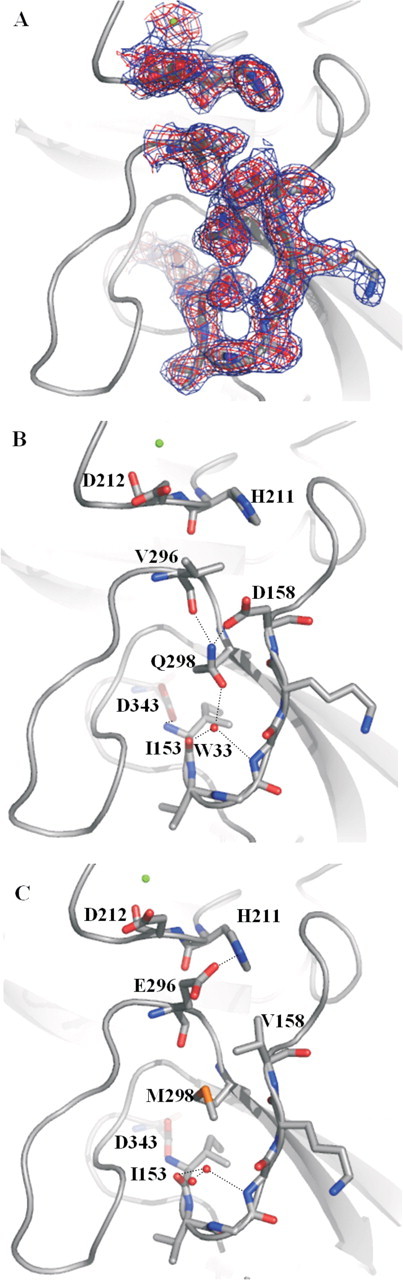
Highlight of residues surrounding positions 158, 296, and 298 in the protease domain in the structures of FVIIaDVQ (2.2 Å) and wild-type FVIIa (2.0 Å; PDB code 1DAN). A,2Fo – Fc electron density shown at 1σ (blue) and 2σ (red). B, the introduced residues Asp158 and Gln298 are part of a distinct hydrogen bond network, including water molecule W33 (in red), leading to increased stabilization and burial of the N terminus and establishment of the salt bridge between Ile153 and Asp343. Such a network is not present in the wild-type structure (C) where Met298 occupies a central position via its hydrophobic nature. Note changes in the interface between the Ca2+-binding loop (Ca2+ shown as a green sphere) and the activation loop via the Val296 mutation, including lack of a hydrogen bond with His211 and a changed rotamer state of Asp212. Root mean square displacements (Cα) of the Ca2+-binding loops of the mutant structure versus the wild-type structure were 0.41 Å compared with an overall of 0.43 Å for the heavy chains.
