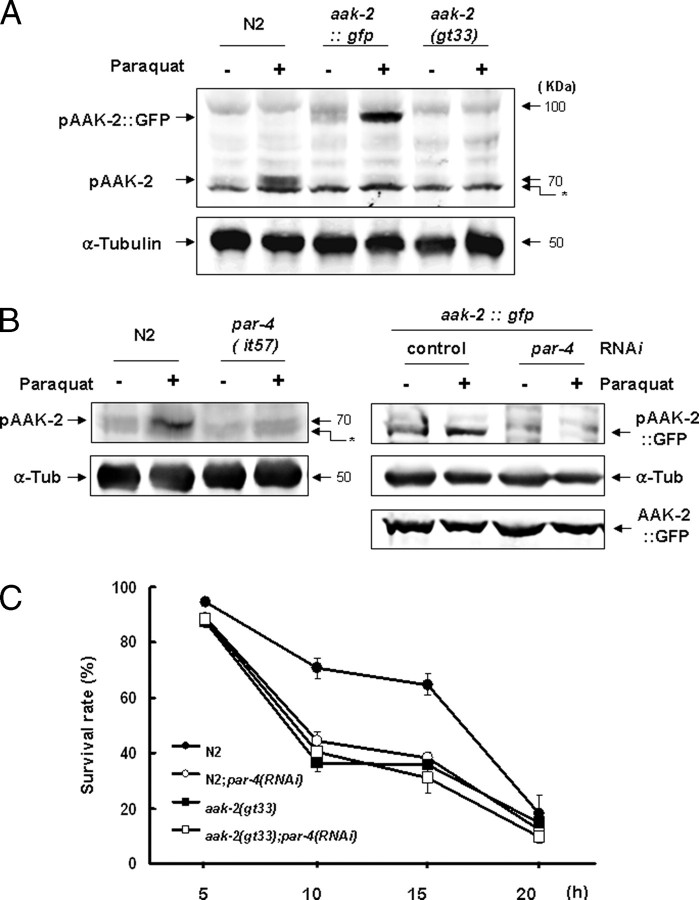
FIGURE 2.
Genetic interaction of aak-2 and par-4 in AAK-2 phosphorylation and worm survival after paraquat treatment. A, phosphorylation of AKK-2 after paraquat treatment of wild-type N2, an aak-2::gfp-overexpressing line, and aak-2(gt33). First-day adult worms were exposed to 100 mm paraquat for 2 h, and worm extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to phospho-AMPK α and α-tubulin as a loading control. Arrows indicate the positions of molecular mass standard proteins of 70 and 50 kDa. The band marked with an asterisk is present even in the aak-2 deletion mutant gt-33, indicating that it is unrelated to aak-2. B, phosphorylation of AAK-2 after paraquat treatment in N2 and par-4 mutant strains and of AAK-2::GFP with or without par-4 RNAi. Anti-GFP rabbit antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used to probe AAK-2::GFP. α-Tub, α-tubulin. C, survival of C. elegans worms with single or double deficiency of aak-2 and par-4. C. elegans worms were incubated in 100 mm paraquat, and survival was scored at 5-h intervals. p > 0.05 for all pairs of single and double deficient strains at 10 and 15 h. Fifty worms were treated with paraquat for each strain, and the experiment was performed three times. Error bars are S.E.