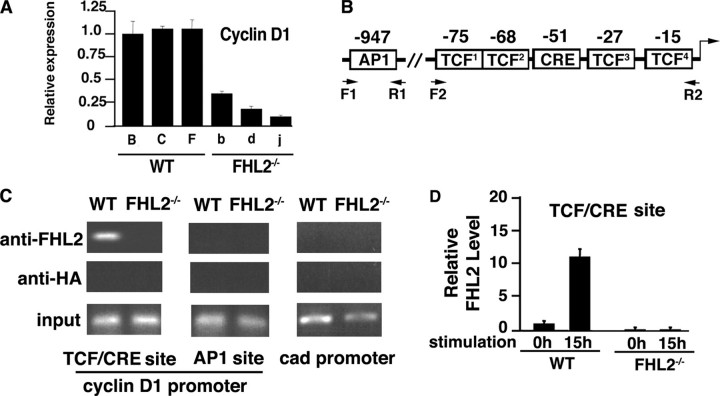
FIGURE 1.
FHL2 is associated with the cyclin D1 promoter. A, analysis of cyclin D1 transcripts in three independent WT and FHL2-/- immortalized clones by real time RT-PCR. Cyclin D1 expression was normalized to 18 S RNA. The ratio of the cyclin D1/18 S signal in WT clone B was arbitrarily set at 1. The average S.D. values and for three independent experiments are shown. Wild type clones are indicated by capital letters, and FHL2-/- clones are shown by lowercase letters. B, schematic representation of AP1 and TCF/CRE elements at the cyclin D1 promoter. C, association of FHL2 with the cyclin D1 promoter at the TCF/CRE site. WT and FHL2-/- MEFs were analyzed by ChIP. Antibodies against FHL2 and HA were used in parallel immunoprecipitations. Eluted DNA was amplified by PCR using cyclin D1 primers F1-R1 and F2-R2 indicated in B and control primers of the cad promoter (see “Experimental Procedures”). Data are representative of three independent experiments. D, graphic representation of the data of real time PCR for the TCF/CREB binding site in immortalized wild type and FHL2-/- MEFs. Calculation of the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA relative to that present in total input chromatin (percentage of total) is as follows: % total = 2ΔCT (where CT represents cycle threshold). ΔCT = CT (input) - CT (FHL2IP). The total percentage at the 0 h time point of serum stimulation in WT MEFs was arbitrarily set at 1. Two independent immortalized FHL2-/- clones were analyzed in two independent ChIP experiments.