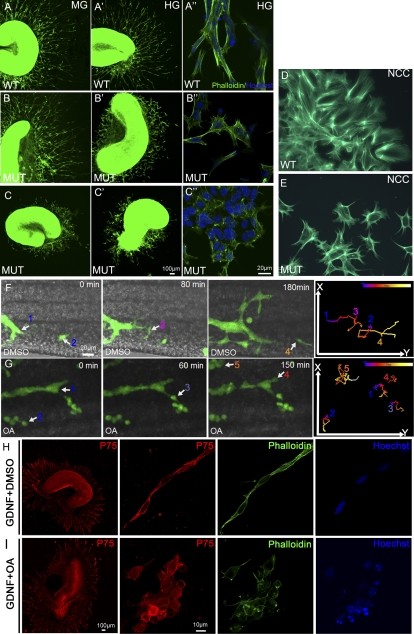
Figure 3.
Phactr4 and PP1 act cell-autonomously to control directed migration. (A–C) Segments of E13.5 proximal midgut (MG) (A–C) and distal hindgut (HG) (A′–C′) were cultured in 3D collagen matrix with GDNF for 3 d and stained with phalloidin (green) to detect the cytoskeleton and with Hoechst (blue) for nuclei. Explants of wild-type gut showed extensive migration of ENCCs out of both gut segments (A,A′). Phactr4humdy ENCCs are responsive to GDNF, but their migration out of the explant is variable. (C,C′) In severe cases, cells from the midgut and hindgut displayed limited migration. (B,B′) In mild cases, only cells from hindgut displayed a migration defect. (A″–C″) Higher magnification of wild-type ENCCs showed elongated cells that migrate together in chains (A″), while Phactr4humdy ENCCs had altered cell shape with random protrusions (B″,C″). (D,E) Vagal NCCs labeled with phalloidin 48 h after migrating from vagal neural tube explant. Wild-type NCCs are elongated and polarized (D), while Phactr4humdy NCCs had aberrant cell shape with random protrusions (E). (F,G) Still images from time-lapse movies of E12.5 wild-type;RetTGM/+ hindgut explants treated with DMSO (F) or 100 nM OA (G) for 3 h, then OA was removed and fresh medium was added, followed by time-lapse imaging over 8 h. Time is noted in minutes. Following OA treatment, cells displayed undirected cell protrusions and random cell movements. Numbers indicate different cells tracked over 8 h at 5-min intervals, and the tracks shown in the right panels are color-coded to indicate the relative time point. (H,I) Explants of wild-type gut cultured with GDNF for 2 d and then treated with DMSO (H) or 20 nM OA (I) for 1 h. (H) In the control explant, ENCCs were polarized and maintained long chains. (I) Inhibition of PP1 activity with OA resulted in altered cell shape with random protrusions. Red is anti-p75NTR antibody detecting the ENCC, green is phalloidin detecting the cytoskeleton, and blue is Hoechst detecting nuclei.