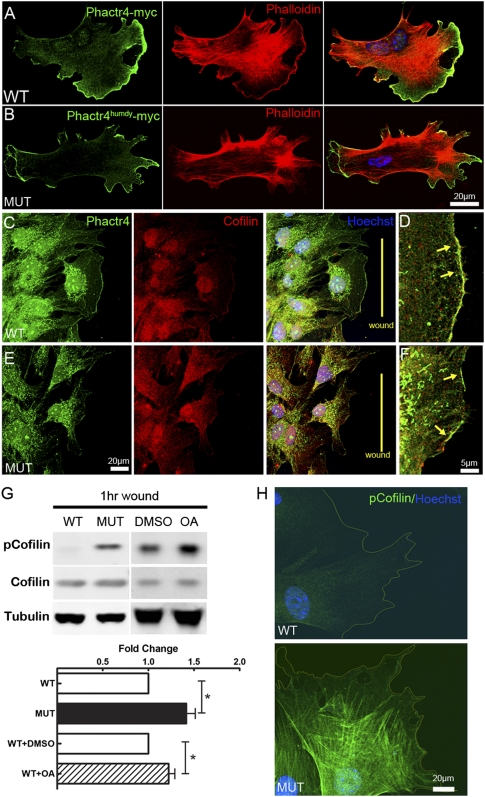
Figure 5.
Cofilin activity is disturbed in Phactr4humdy MEFs. (A,B) Myc-tagged Phactr4 wild-type (A) or humdy (B) construct was transfected into wild-type or mutant MEFs, respectively. MEFs were fixed and stained with anti-Myc antibody, phalloidin, and Hoechst, showing Phactr4 localization to the lamellipodium. (C–F) Detection of endogenous Phactr4 protein, with an anti-Phactr4 antibody (green) showing colocalization with cofilin (red) at the leading edge of lamellipodium in wounded wild-type (D) or mutant (E) MEFs. The arrow shows colocalization at the lamellipodium. (G) MEFs were grown to confluency in a laminin-coated dish for 36 h and then wounded extensively (evenly spaced wounds, 500 μm apart). Cells were allowed to migrate into the wound for 1 h. Where indicated, 0.1 μM OA or DMSO was added to wild-type MEFs during the wound healing period. Western blot analysis of total lysates with the indicated antibodies is shown. Quantification of protein expression showed 46% increase of pSer-cofilin in mutant and 26% increase in OA-treated wild-type cells. n = 6; (*) P < 0.05. (H) Immunostaining of pSer3-cofilin in wounded wild-type (top panel) and mutant (bottom panel) MEFs.