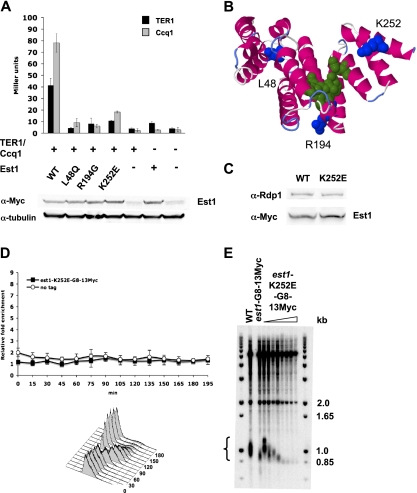
Figure 6.
Est1 telomere maintenance and binding requires the 14-3-3-like domain. (A) Quantification of TER1 and Ccq1 interaction with Est1 mutants by RNA three-hybrid and two-hybrid analysis. Wild-type Est1 and mutations in the 14-3-3-like domain of Est1 were generated by error-prone PCR. Wild-type and Est1 mutants were expressed in the pACT2 (three-hybrid analysis) and pGBKT7 (two-hybrid analysis) vectors. RNA three-hybrid analysis was used to monitor Est1 wild-type or mutant protein interaction with TER1, and two-hybrid analysis was used to monitor Est1 wild-type or mutant protein interaction with Ccq1. Nucleotides 415–507 of TER1 were expressed from the pIII/ms2-2 vector, and Ccq1 was expressed from pACT2. Quantification of interaction strengths in Miller units was determined by a β-galactosidase assay for both three-hybrid and two-hybrid analyses. Est1–TER1 interactions are depicted in black, and Est1–Ccq1 interactions are depicted in gray. Error bars represent standard deviation for n = 3. Stability of the mutant est1 proteins was demonstrated by Western blotting of lysates from two-hybrid analysis. α-tubulin levels are a loading control. (B) Predicted protein structure of the Est1 14-3-3-like domain (amino acids 1–260) generated by Phyre2 using normal modeling mode (Kelley and Sternberg 2009). Amino acids L48, R194, and K252 are colored blue. Conserved residues (R79, R180, Y181, and Q215) that are predicted to be involved in phosphoserine binding (Fukuhara et al. 2005) are colored green. (C) Western blotting demonstrates stability of Est1-G8-13Myc and Est1-K252E-G8-13Myc. (D) Est1-K252E-G8-13Myc does not associate with telomeres. Synchronous ChIP was performed on cells expressing Est1-K252E-G8-13Myc as described in Figure 5 (n = 3). (E) est1-K252E-G8-13Myc causes rapid telomere loss. Telomere blot of successive streaks of cells expressing Est1-K252E-G8-13Myc compared with wild-type telomere length and telomeres in cells expressing Est1-G8-13Myc.