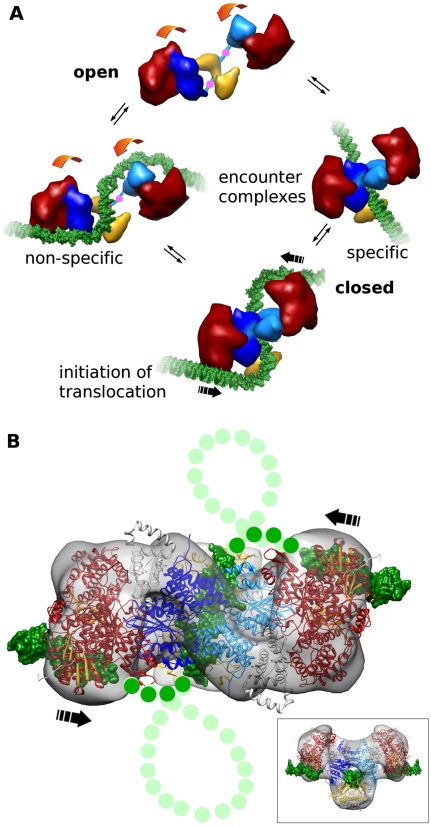
Figure 6.
Schematic of large-scale conformational change and initiation of DNA looping and translocation. (A) Type I RM enzymes exist in a dynamic equilibrium between open and closed states (movement is shown by orange arrows, and pivot points in C-terminal regions of HsdM are indicated by pink dots). DNA (green) binding to form encounter complexes can occur nonspecifically to the HsdR (red) or via the target sequence to the MTase core (HsdM is in light and dark blue, and HsdS is in yellow). Complete closure of the enzyme and bending of the DNA around the HsdR produces the initiation complex for DNA translocation. (B) The predicted complete path of the DNA (green dots) through the atomic model of EcoR124I with segments of bound DNA. This is the proposed initiation complex (from Fig. 5A). During active translocation, the DNA would then form expanding loops from each side (light-green dots for DNA, and the direction of translocation is shown by black arrows). The inset shows the initiation complex turned 90° to the main panel.