Figure 2.
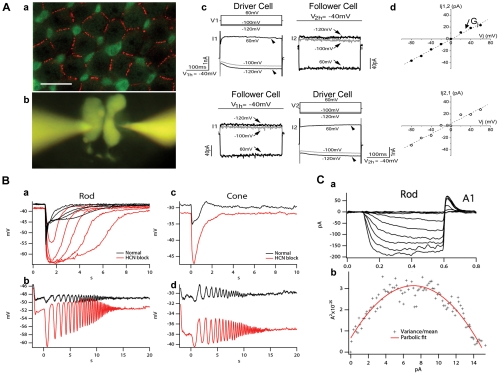
Electrical coupling and HCN1 channels in salamander photoreceptors. (Aa) Confocal image of a salamander flatmount retina (with the focal plane at the level of the distal region of rod cell bodies) double labeled with anti-Cx35/36 (red) and recoverin (green). Recoverin differentially labeled rods (r, weak green) and cone inner segments (c, strong green). The strong Cx35/36 punctate labeling on membrane contacts outlined the mosaic of the rod network in the field. Scale bar, 20 μm. (Ab) A pair of rods simultaneously patch clamped and filled with Lucifer yellow through two recording pipettes. (Ac) Simultaneous dual whole-cell voltage clamp recordings from a pair of neighboring rods. The membrane potential of two rods was held at −40 mV. Upper panel: when a series of voltage step commands (V1) (from −120 mV to 60 mV with an increment of 20 mV) were applied to cell 1 (driver cell), the voltage activated current responses (I1) (arrowheads) were recorded in cell 1 (left panel) and the junctional currents of the opposite polarity (I2) (arrows) were recorded in cell 2 (follower cell, right panel). Lower panel: switching the position of driver/follower cells. (Ad) Relations of transjunctional current (Ij) and transjunctional voltage (Vj) obtained in upper and lower panels in (Ac). The junctional conductance (Gj) measured in either direction is 500 pS. (Reprinted from Zhang J, Wu SM. Physiological properties of rod photoreceptor electrical coupling in the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol. 2005;564:849–86. © 2005 by The Physiological Society.) (Ba) Rod responses to flashes of increasing light intensity in normal Ringer's (black traces) and in the presence of 100 μM HCN channel blocker ZD 7288 (red traces). (Bb) Rod response to a frequency-chirped light stimulus (chirped sine wave-modulated light ranged from 0.5 to 5 Hz over the course of 20 seconds) in normal Ringer's (black) and in 100 μM ZD 7288 (red). (Bc, Bd) Cone responses to flashes of increasing light intensity (Bc) and to frequency-chirped light stimulus (Bd) in normal Ringer's (black traces) and in the presence of 100 μM ZD 7288 (red traces). (Ca) Whole-cell recording of HCN channels from a rod to hyperpolarizing voltage steps with an extracellular solution containing TEA, cobalt and barium so that all other ionic currents other than Ih were blocked. (Cb) Variance versus mean plot computed from an ensemble of whole-cell Ih current. The slope of the variance-mean plot at 0 mean current gives an estimate of single channel conductance of 663 ± 71 fS, and the peak of the hyperbolic curve gives an estimate of the total number of HCN1 channels per rod of 2214 ± 986. (Part C reprinted with permission from Barrow AJ, Wu SM. Low-conductance HCN1 ion channels augment the frequency response of rod and cone photoreceptors. J Neurosci. 2009;29:5841–5853. © 2009 by the Society for Neuroscience.)