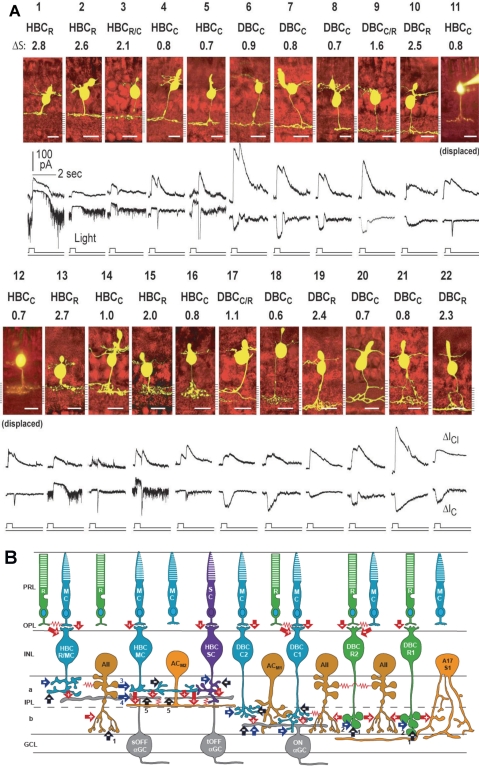
Figure 3.
(A) Stratum-by-stratum rules for correlating patterns of axon terminal ramification and physiological responses in retinal bipolar cells. 22 morphologically identified (by Lucifer yellow filling) BCs and their light-evoked excitatory cation current (ΔIC) and inhibitory chloride current (ΔICl) recorded from dark-adapted salamander retinal slices. Each cell is named according to their spectral difference (ΔS) and ΔIC polarity as rod-dominated, cone-dominated, mixed rod/cone hyperpolarizing or depolarizing bipolar cells (HBCR, HBCC, HBCR/C, DBCR, DBCC or DBCR/C). BCs with inward ΔIC are DBCs and with outward ΔIC are HBCs. The spectral difference, ΔS, is defined as S700 − S500 (where S700 and S500 are intensities in log units of 700- and 500-nm light eliciting responses of the same amplitude). Since ΔS for the salamander rods is approximately 3.4 and that for the cones is approximately 0.1, BCs with ΔS > 2.0 are rod-dominated (HBCR or DBCR), with ΔS < 1.0 are cone-dominated (HBCC or DBCC), and with 1.0 < ΔS < 2.0 are mixed rod/cone cells (HBCR/C or DBCR/C, also named HBCM or DBCM, see Fig. 4). Displaced HBCCs: HBCCs with somas displaced in the outer nuclear layer. (Modified from Pang J-J, Gao F, Wu SM. Stratum-by-stratum projection of light response attributes by retinal bipolar cells of Ambystoma. J. Physiol. 2004;558:249–262. © 2004 by The Physiological Society; and Maple BR, Zhang J, Pang J-J, Gao F, Wu SM. Characterization of displaced bipolar cells in the tiger salamander retina. Vision Res. 2005;45:697–705. © 2005 Elsevier Ltd.) (B) Schematic diagram of synaptic connections of photoreceptors, BCs, ACs, and α GCs in the mammalian retina. R, rod; MC, M-cone; SC, S-cone; HBCMC/R, mixed M-cone/rod hyperpolarizing BC; HBCMC, M-cone dominated hyperpolarizing bipolar cell; HBCSC, S-cone dominated hyperpolarizing bipolar cell; DBCC2, type 2 cone depolarizing bipolar cell; DBCC1, type 1 cone depolarizing bipolar cell; DBCR2, type 2 rod depolarizing bipolar cell; DBCR1, type 1 rod depolarizing bipolar cell. Note that BCs with the most rod inputs have axon terminal endings near the two margins of the IPL, whereas those with the most cone inputs bear axons ramifying in the central regions of the IPL, similar to the rules set forward by the salamander BCs (A). ACM1, M-cone dominated depolarizing amacrine cell; ACM2, M-cone dominated ON-OFF amacrine cell; AII, AII amacrine cell; A17/S1, A17 amacrine cell; sOFFαGC, sustained OFF αGC; tOFFαGC, transient OFF αGC; ONαGC, ON αGC; green: rods and rod BCs; blue: M-cones and M-cone BCs, purple: S-cone and S-cone BCs; light orange: GABAergic ACs; dark orange: glycinergic ACs; gray: αGCs; arrows: chemical synapses (red, glutamatergic; black, GABAergic; blue, glycinergic; +, sign-preserving; −, sign-inverting); zigzag (red): electrical synapses. PRL, photoreceptor layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer (a, sublamina a, b, sublamina b); GCL, ganglion cell layer. Many inhibitory synapses from unspecified ACs are represented as black and blue arrows.