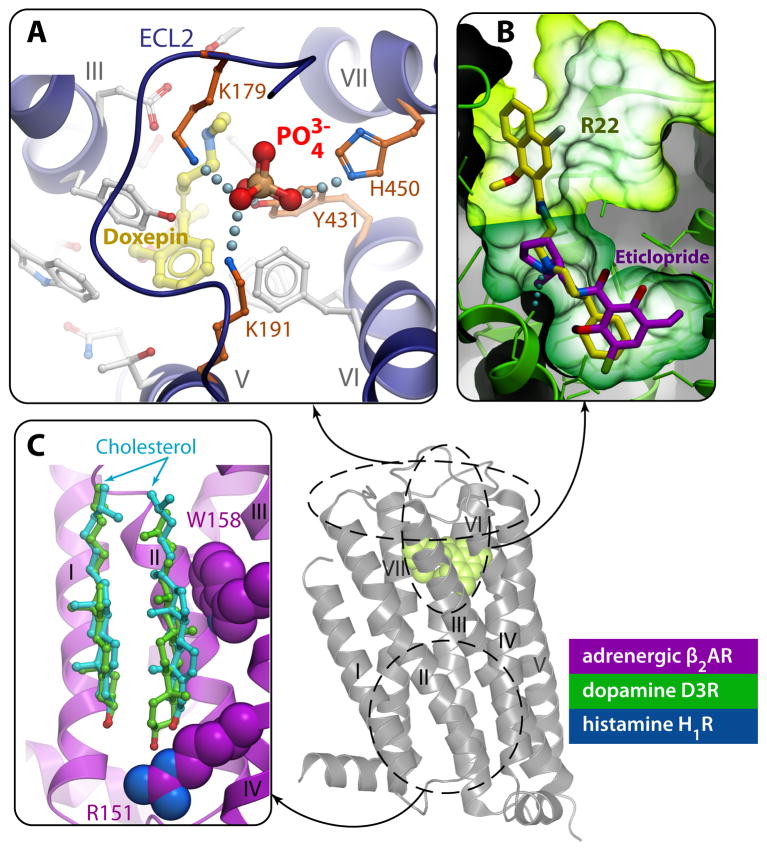
Fig. 6.
Examples of allosteric interaction sites identified in GPCR crystal structures. A) Binding of a phosphate ion in the ECLs of H1R (PDB ID 3RZE) is coordinated by four receptor side chains, and affects the accessibility of the ligand pocket. This site is key for H1 subtype selectivity to second-generation antihistamines [18]. B) The ligand-binding pocket in the D3R (PDB ID 3PBL) consists of a core site (dark green) with bound antagonist eticlopride and a secondary or allosteric site (lime). Docking the D3 subtype-selective ligand R22 into the D3R crystal structure reveals the bitopic nature of this compound occupying the core site and extending into the secondary site. Interactions between R22 and the secondary site define most of the subtype selectivity for this ligand [17]. C) The cholesterol binding site on the lipid-TM interface has been reproduced in different crystal forms of the β2AR, (shown here by cyan sticks for PDB IDs 2RH1 and by green sticks for 3D4S), and is likely conserved in many other GPCRs [23].